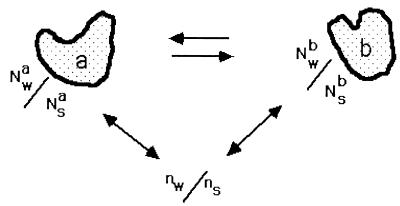
Figure 1.
Dilute macromolecules are equilibrated with a bulk solution that contains a ratio ns/nw of solute to water. In a region around the macromolecule, the ratio of solute to water, Ns/Nw, can be different from the bulk for various reasons. If this ratio is different between two conformations of the macromolecule, here labeled a and b, then the effect of solute or water chemical potential on the equilibrium can be described by Eq. 5. Ns and Nw are to be considered in the nature of an integrated Gibbs excess or deficit (Appendix), i.e., how Ns/Nw differs from ns/nw.