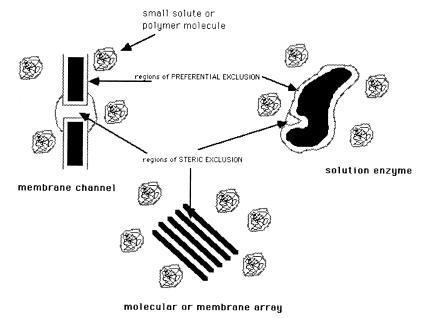
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of how solutes can produce osmotic stress on a variety of systems as a result of their exclusion. Solute can be sterically excluded from water-filled cavities, grooves, channels, or other such enclosed volumes. The crowding and preferential hydration viewpoints are specifically concerned with the exclusion of solutes from exposed macromolecular surfaces.