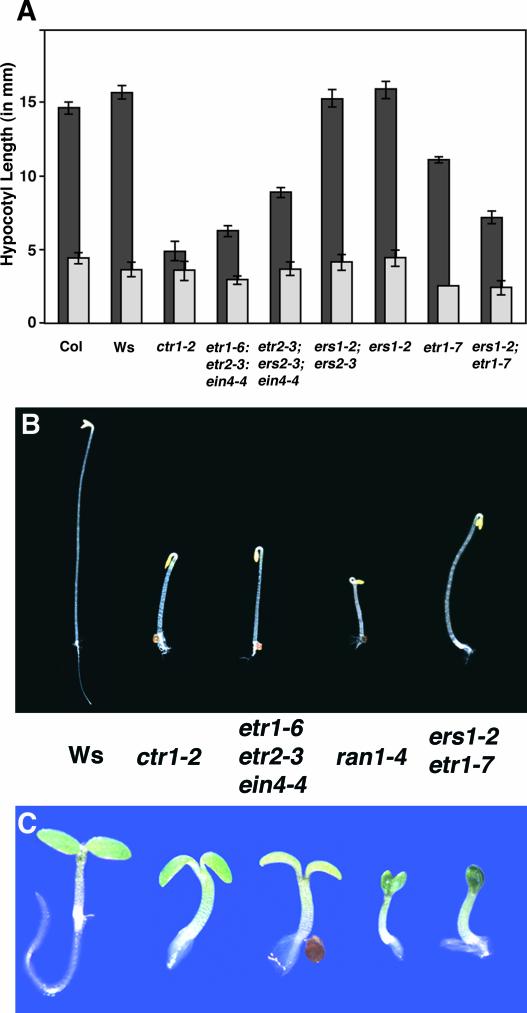
Figure 1.
Light-Grown ers1 etr1 Mutants Exhibit a Severe Constitutive Ethylene-Response Phenotype, Whereas Dark-Grown Seedlings Exhibit a Partial Ethylene-Response Phenotype.
(A) ers1 etr1 mutants are capable of responding to ethylene. Hypocotyl lengths (in mm) of etiolated seedlings grown for 4 days in either air (dark gray) or 35 ppm of ethylene (light gray) are shown. At least 15 seedlings were measured for each treatment. ers1 etr1 mutants were identified phenotypically once the plates were removed from the dark and left in the light for 7 days. Col, Columbia wild type.
(B) Seedlings grown in the dark on agar plates for 4 days in air. Compared with other constitutive response mutants, ers1 etr1 seedlings exhibited only a partial inhibition of hypocotyl growth but a more complete inhibition of root growth relative to wild-type (Ws) seedlings.
(C) Seedlings grown in the light for 3 days in air. Ws seedlings appear wild type, whereas the ctr1 and etr1 etr2 ein4 mutants exhibit shorter hypocotyls, short roots with prolific root hairs, and smaller, less expanded cotyledons than wild-type seedlings. The ers1 etr1 mutants phenocopied the severe ran1 mutants, exhibiting shorter hypocotyls and roots and small, dark, unexpanded cotyledons.