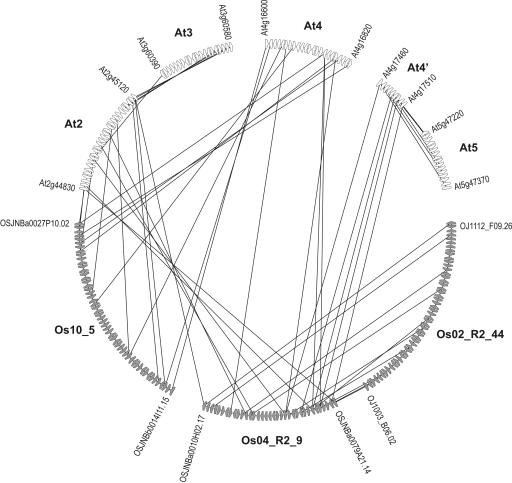
Figure 6.
Set of Homologous Chromosomal Segments (Multiplicon) of Arabidopsis and Rice.
Arrows represent the genes on the chromosomal segments, and connecting lines indicate the anchor points (i.e., homologous or duplicated genes) that are part of a significant colinear relation determined by the ADHoRe algorithm. For each genomic segment, the names of the two genes delineating the segment are shown. Chromosomal segments of rice and Arabidopsis are shown in gray and white, respectively. By considering the colinearity between Arabidopsis and rice, a set of seemingly unrelated Arabidopsis segments can be joined into a multiplicon with a multiplication level of five, confirming the three duplication events in Arabidopsis described previously (Simillion et al., 2002). This colinearity also reveals that all three rice segments are linked with each other by two duplication events. Scaffold Os04_R2_9 includes BACs with accession numbers AL663006, AL662998, AL606459, AL607006, AL606728, AL606695, AL606587, AL606647, AL606633, AL663000, AL731613, AL606682, AL606687, AL606694, AL606628, AL607001, AL663003, and AL662954; scaffold Os10_5 includes BACs with accession numbers AC084763, AC079890, AC079874, AC069300, AC037426, and AC026758; and scaffold Os02_R2_44 includes BACs with accession numbers AP005108, AP004037, AP004883, AP005072, AP005289, AP005006, and AP004676.