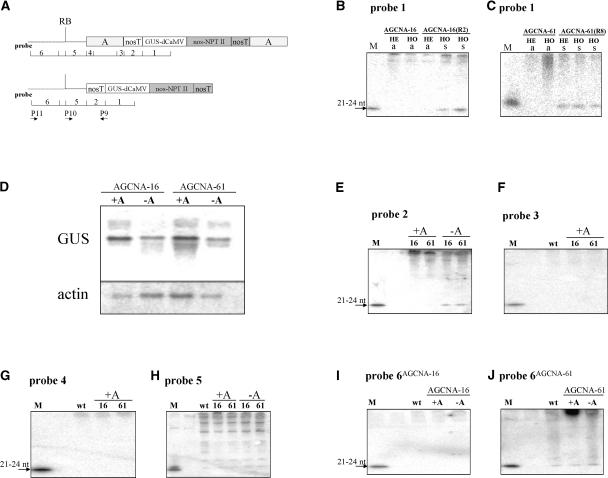
Figure 7.
GUS Gene Silencing Involves Plant Flanking DNA.
(A) Schemes of the T-DNA in +A and −A transgenic plants with the positions of probes 1 to 6 used for the detection of siRNAs. The primers used for cDNA synthesis and RT-PCR are indicated. RB, right border.
(B) Phosphorimage of the small RNA fraction from active (a) hemizygous (HE) and homozygous (HO) AGCNA-16 plants and silenced (s) homozygous (HO) AGCNA-16(R2) plants after hybridization with probe 1. Small RNA only is seen in the silenced plants. nt, nucleotides.
(C) The same as in (B) in a silenced HE and HO AGCNA-61(R8) plant.
(D) RNA gel blot analysis of total RNA using GUS and actin gene probes. For analysis, a 10-fold higher amount of RNA from silenced plants was used to compensate for the reduced steady state level of RNA.
(E) to (J) Detection of siRNAs with the probes indicated at top. Line AGCNA-16 is indicated as 16, and line AGCNA-61 is indicated as 61. Flanking DNA of AGCNA-16 is indicated as probe 6AGCNA-16, and flanking DNA of AGCNA-61 is indicated as probe 6AGCNA-61. In all cases, lanes labeled M contain an oligomer from a particular probe (ranging in size from 21 to 24 nucleotides) that functions as a size marker and a positive control for hybridization. The lanes labeled wt contain RNA from wild-type tobacco.