Abstract
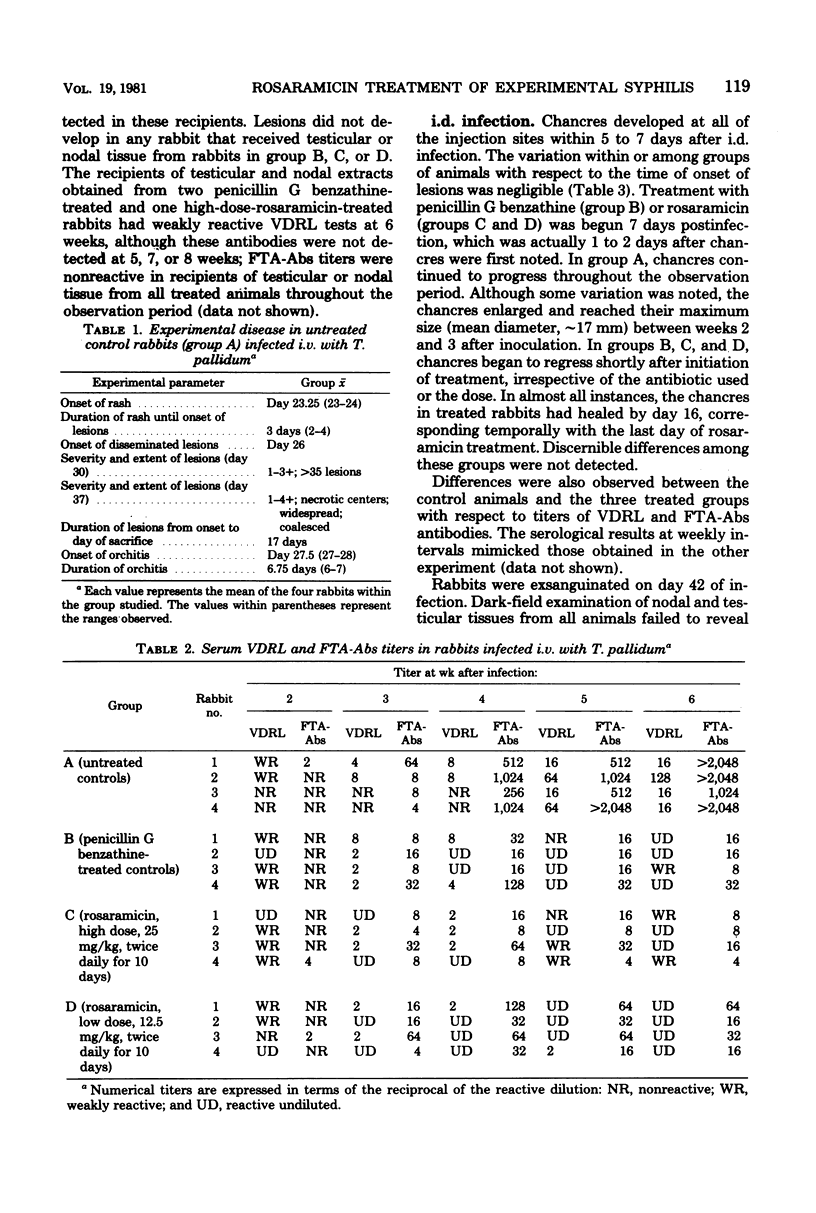
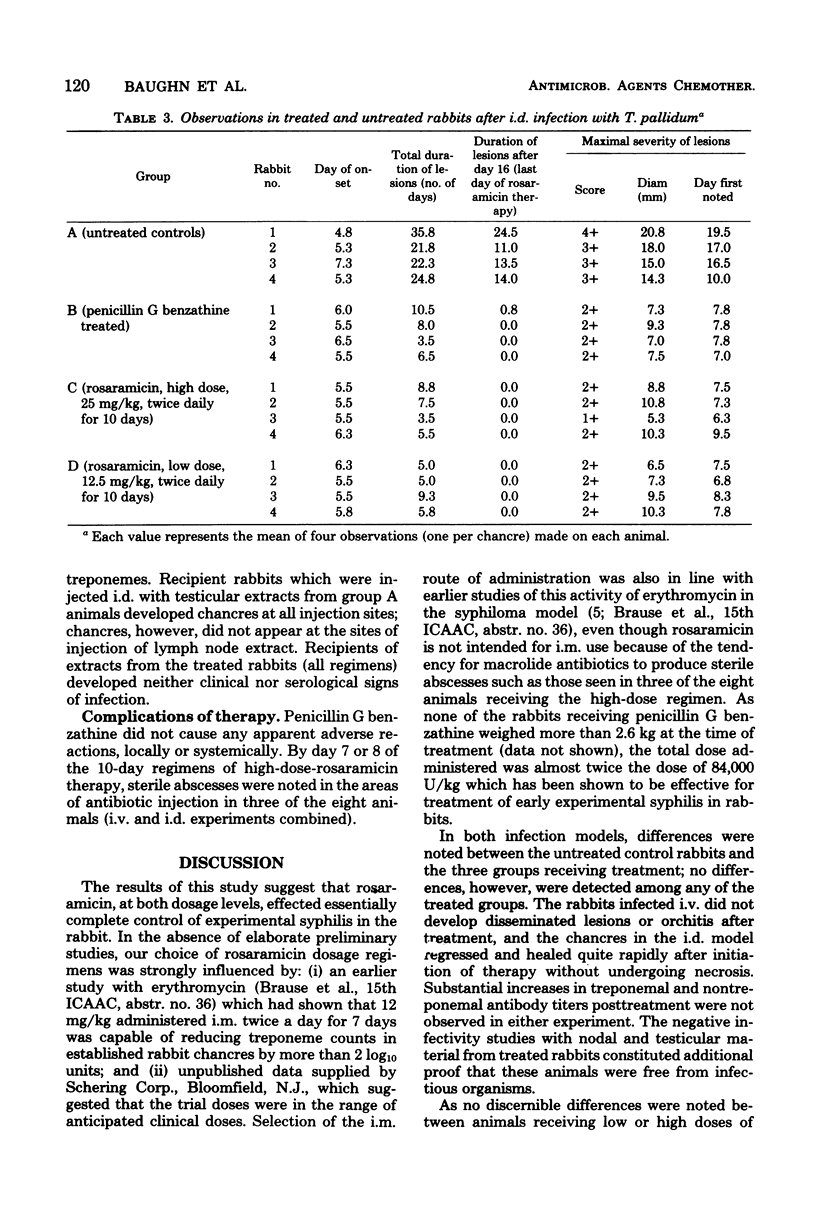
The in vivo activity of rosaramicin phosphate in disseminated and localized Treponema pallidum infections in rabbits was compared with that of penicillin G benzathine. Rabbits were injected either intradermally or intravenously to establish infection. Groups of four animals each then received either two weekly injections of 200,000 U of penicillin G benzathine, injections of 12.5 or 25 mg of rosaramicin per kg of body weight twice a day for 10 days, or no antibiotic therapy. Treatment of the intradermal and intravenous infections was initiated on days 7 and 14 postinfection, respectively. With both infection models, striking differences were noted between the untreated control rabbits and the three groups receiving treatment; no discernible differences, however, were detected among any of the treated groups. Rabbits that had been infected intravenously did not develop disseminated lesions or orchitis after treatment, and chancres produced by intradermal infection regressed and healed rapidly after the initiation of therapy. Continued increases in treponemal and nontreponemal antibody titers posttreatment did not occur in any of the treated rabbits. Infectivity studies also suggested that the lymph nodes and testes of treated animals were free from infectious organisms. Overall, at the dosage regimens employed, both rosaramicin and penicillin G benzathine appeared to effect complete control of the experimental disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Aberrant secondary antibody responses to sheep erythrocytes in rabbits with experimental syphilis. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):133–138. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.133-138.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Korbut S. E., Bednova V. N., Timcenko G. F., Milonova T. I. Long-term results of penicillin treatment of early and late forms of syphilis in the rabbit. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Oct;49(5):413–419. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.5.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER T. B., SCHAEFFER K. The comparative effect of various antibiotics in experimental syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Mar;38(2):81–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagman G. H., Waitz J. A., Marquez J., Murawaski A., Oden E. M., Testa R. T., Weinstein M. J. A new Micromonospora-produced macrolide antibiotic, rosamicin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Nov;25(11):641–646. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Drube C. G., Moss E. L., Jr, Weinstein M. J. Biological studies with rosamicin, a new Micromonospora-produced macrolide antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Nov;25(11):647–652. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


