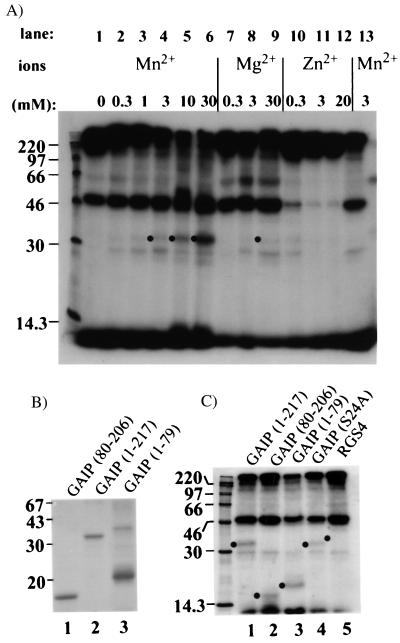
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of GAIP by CCVs. (A) His6 GAIP (lanes 1–12) was mixed with [γ32-P]ATP, in the absence (lane 1) or presence of increasing concentrations of Mn2+ (lanes 2–6 and 13), Mg2+ (lanes 7–9), or Zn2+ (lanes 10–12). Reactions were started by addition of CCVs and stopped with SDS/BSA. Proteins were acetone precipitated, separated by 12.5% SDS/PAGE, and exposed for autoradiography. Phosphorylation of recombinant GAIP (dots) is favored by Mn2+ (lanes 4–6). (B) Migration of recombinant GAIP. His6-tagged proteins were analyzed by SDS/PAGE on a 15% polyacrylamide gel, and stained with Coomassie blue R-250. Migration of GAIP80–206 (lane 1), wild-type GAIP (lane 2), and GAIP1–79 (lane 3) are shown. The N terminus of GAIP, GAIP1–79, migrates more slowly than expected. (C) Phosphorylations were performed as in A in the presence of 3 mM MnCl2 and with the following His6-tagged proteins: wild-type GAIP (lane 1), GAIP80–206 (lane 2), GAIP1–79 (lane 3), GAIP (S24A) (lane 4), or RGS4 (lane 5). Phosphorylated recombinant proteins are marked with a dot. Phosphorylation in the presence of CCVs occurs at the N terminus (1–79) and in the RGS domain (80–206) of GAIP. Mutation of Ser-24 reduced the phosphorylation of GAIP.