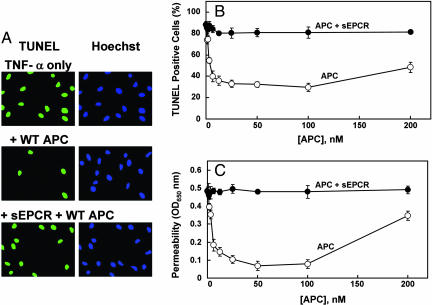
Fig. 2.
Antiapoptotic and cytoprotective activities of APC in TNF-α-induced apoptosis and permeability assays in EA.hy926 cells. (A) Confluent monolayers of EA.hy926 cells were treated with APC (10 nM) in either the absence or presence of a saturating concentration sEPCR (500 nM) for 24 h followed by induction of apoptosis with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 4 h. The cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and incubated with the TUNEL reaction mixture followed by Hoechst 33342 to stain the apoptotic cells (green) and the total number of nuclei (blue), respectively. (B) The same as above except the number of apoptotic cells is expressed as the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells of the total number of nuclei (P < 0.001) as a function of various concentrations of APC in the absence (○) and presence (●) of sEPCR. (C) The APC concentration dependence of inhibition of thrombin-induced permeability in the absence (○) and presence (●) of sEPCR was monitored from the flux of Evans blue-bound albumin across EA.hy926 cells as described in Materials and Methods.