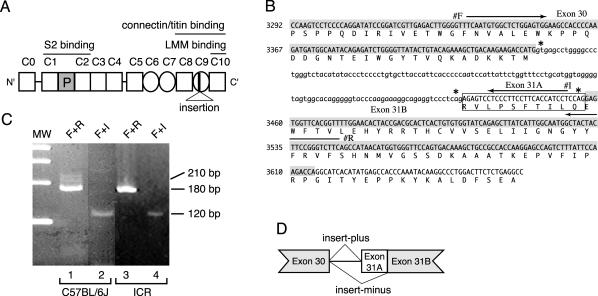
Figure 1.
(A) Structure of mouse cardiac MyBP-C protein (cMyBP-C). The numbers above cMyBP-C indicate the position of each IgI domain (open square) and FN type III repeat (circle). The cardiac-specific phosphorylation domain is shown as a shaded square (P). Position of 10 amino acids insertion is indicated in C9 domain. (B) Genomic sequence and deduced amino acid sequence encoding the C9 IgI domain of mouse cardiac MyBP-C. The nucleotide sequence of the coding region and the deduced amino acid sequence of MyBP-C(+) are represented in capital letters. Exon 30 and 31B are highlighted by hatch. MyBP-C(+)-specific insert sequence (exon 31A) is indicated by a box. Arrows indicate the location of primer F (#F), primer I (#I) and primer R (#R). Asterisks indicate a 5′ splice donor sequence, gt, and 3′ splice acceptor sequence, CAG. (C) Identification of MyBP-C(+) in C57BL/6J and ICR mice. cDNA libraries prepared from 8-wk-old C57BL/6J hearts (lane 1 and 2) or from ICR hearts (lane 3 and 4) were subjected to PCR by using a primer F + R set (lane 1 and 3) or using a primer F + I set (lane 2 and 4). Primer F + R set amplifies 212-base pair and 182-base pair DNA fragments which are generated from MyBP-C(+) and MyBP-C(–) cDNA, respectively. Primer F + I set specifically detects MyBP-C(+) cDNA as a 118-base pairs product. A molecular weight marker (MW) indicates 400, 300, 200, and 100 base pairs, top to bottom. (D) Schematic genomic structure of mouse cardiac MyBP-C. Both MyBP-C(–) and MyBP-C(+) mRNAs are encoded by a single gene and generated by an alternative mRNA splicing.