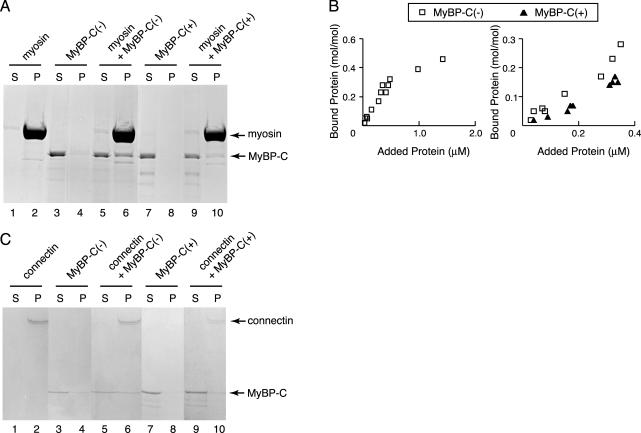
Figure 2.
Binding of recombinant MyBP-C to myosin filaments or connectin/titin. (A) Cosedimentation assays were performed using 0.5 μM of cardiac myosin filaments and 0.15 μM MyBP-C(–) or 0.17 μM MyBP-C(+) at 0.1 M KCl. Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) were separated by centrifugation, followed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining. Arrow indicates position of myosin or MyBP-C. (B) Left, equilibrium binding reactions between MyBP-C(–) and cardiac myosin filaments. Different concentrations of MyBP-C (0–1.5 μM) were incubated with a constant concentration (0.5 μM) of cardiac myosin filaments. Samples were separated by centrifugation and dissolved by SDS-PAGE. CBB-stained gels were densitometrically scanned, and the concentrations of bound protein were normalized to the myosin concentrations. Right, binding reactions of MyBP-C (0–0.4 μM) and cardiac myosin (0.5 μM) below the saturated concentration. Open square, binding of MyBP-C(–) to the myosin filaments; closed triangle, binding of MyBP-C(+) to the myosin filaments. (C) Binding assays were performed at 0.04 μM β-connectin and 0.1 μM MyBP-C(–) or 0.13 μM MyBP-C(+) at 0.1 M KCl. (S) and (P) on the SDS-gels stained with CBB represent supernatant and pellet fractions after the centrifugation, respectively. Arrow indicates position of β-connectin or MyBP-C.