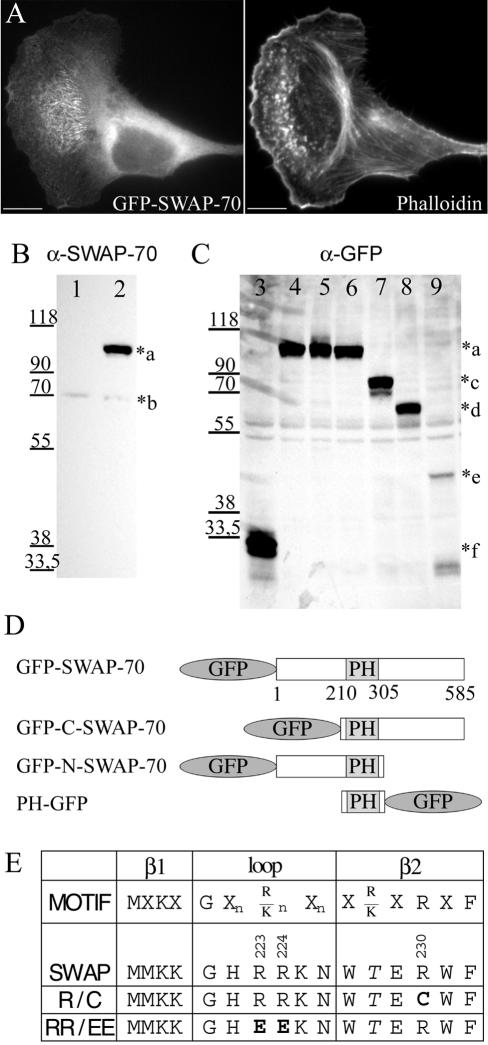
Figure 4.
GFP-constructs. (A) Thirty hours after transfection with GFP-SWAP-70, B16F1 cells were replated on laminin-coated coverslips and after an additional 5 h fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained with Alexa 594-phalloidin. Bars, 10 μm. (B and C) B16F1 cells were transfected with different GFP-SWAP-70-constructs for 30 h and then analyzed by Western blotting with polyclonal affinitypurified SWAP-70 antibody GK2 (B) or monoclonal GFP antibody (C). Equal amounts of protein (B, 10 μg; C, 40 μg) from cell homogenates were loaded. Cells were transfected with the following constructs: lanes 1 and 3: pEGFP-C1; lanes 2 and 4: GFP-SWAP-70; lane 5: GFP-SWAP-R230C; lane 6: GFP-SWAP-RR223,224EE; lane 7: GFP-SWAP(205-585); lane 8: GFP-SWAP(1-313) and lane 9: PH(205-313)GFP. The *a–f indicates the size of the different constructs: a (∼100 kDa): GFP-SWAP-70; b (70 kDa): endogenous SWAP-70; c (∼75 kDa): GFP-SWAP(205-585); d (∼67 kDa): GFP-SWAP(1-313); e (∼43 kDa): PH(205-313)-GFP; and f (∼30 kDa): GFP. (D) Schematic representation of SWAP-70 GFP-fusion proteins. (E) Residues conserved in PH domains binding to PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3 (Isakoff et al., 1998) are aligned to the SWAP-70 sequence. Mutated residues in constructs R230C and RR223,224EE are indicated in bold.