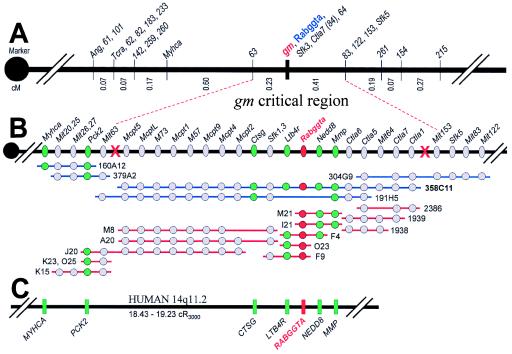
Figure 2.
Genetic and physical maps of mouse chromosome 14 in the vicinity of gm. (A) Consensus genetic map of the gm region on chromosome 14 derived from three backcrosses (MGD J:52722). The circle represents the centromere. Distances between markers are in centimorgans (cM). Numbered loci represent microsatellite markers. Relative positions of loci were ascertained from 769 [(C57BL/6J-gm × SPRET)F1 × C57BL/6J-gm], 727 [(C57BL/6J-gm × PWK)F1 × C57BL/6J-gm], and 966 [(C57BL/6J-gm × DBA)F1 × C57BL/6J-gm] backcross mice. No recombination was found between gm and Rabggta. Dotted lines link the consensus gm genetic map to the physical map. (B) Physical map of the gm nonrecombinant interval (MGD J:52722). The gm critical region is delineated by chromosome crossovers (denoted by red X). gm was flanked by D14Mit63 (proximal), and D14Mit153 and D14Mit122 (distal). YAC (blue lines) and BAC (red lines) clones are shown. Loci physically mapped within YAC and BAC clones are indicated with colored circles. The location of Rabggta is indicated by red circles. Green circles indicate genes near gm that (C) also map to the homologous human chromosomal segment (14q11.2).