Figure 5.
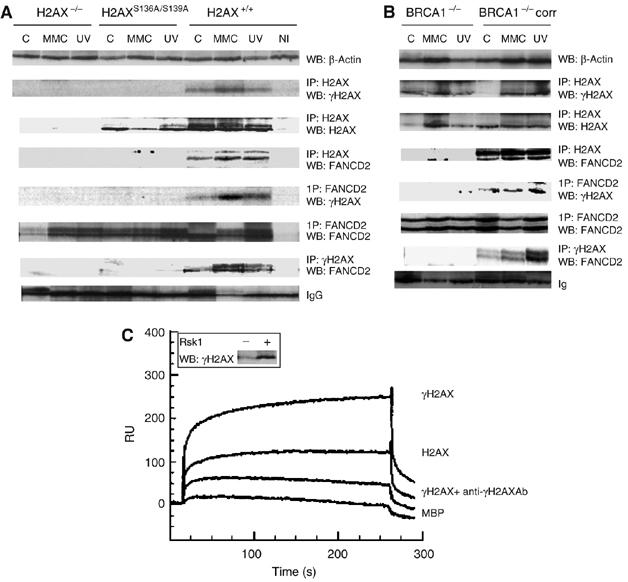
BRCA1-dependent binding of FANCD2 to γH2AX upon DNA damage. FANCD2 co-immunoprecipitates with γH2AX after DNA damage in a BRCA1-dependent manner. H2AX+/+, H2AXS136A/S139A, H2AX−/− MEF (A) or BRCA1−/− and BRCA−/− corrected cells (B) were not treated (−), MMC-treated (MMC) or UVC-irradiated (UV) as described in Materials and methods. Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with γH2AX, H2AX, FANCD2 or non-immune control (NI) antibodies followed by Western blot, and the protein bands were detected by probing with FANCD2, H2AX or γH2AX antibody, respectively. Loading control was monitored either by β-actin Western (A, B, upper row) or nonspecific binding to IgG (A, B, lowest row). Steady-state levels of γH2AX, FANCD2 or β-actin are maintained by Western blot of the corresponding samples before IP. In panels A and B, blots 2–4 and 5–7 represent H2AX IPs and FANCD2 IPs, respectively. Direct binding of FANCD2 to γH2AX by SPR (C). Equal aliquots of H2AX and H2AX phosphorylated by Rsk1 kinase were monitored by Western blot probed with γH2AX antibodies. Binding sensorgram of phosphorylated H2AX to the immobilized FANCD2. FANCD2 was immobilized (5 ng/mm2) on a dextran surface, as described in Materials and methods. Phosphorylated (A), nonphosphorylated (C) or phosphorylated H2AX premixed with anti-γH2AX antibody diluted at 1:500 (B) was injected over immobilized FANCD2. Control binding was performed on an unrelated (MBP) protein surface (C). The double bands of the FANCD2 WB panels in panels A and B correspond to FANCD2L (monoubiquitinated FANCD2; upper band) and FANCD2S (non-monoubiquitinated FANCD2).
