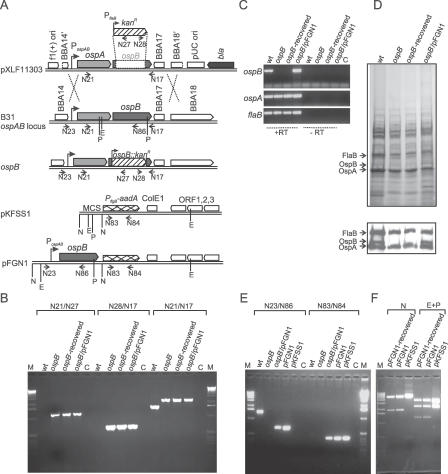
Figure 1. Characterization of the ospB Mutant and the OspB Complemented Mutant.
(A) Strategy for the inactivation of the ospB gene and for the generation of the OspB complemented mutant is shown. The top diagram represents the suicide vector pXLF11303 used for transformation into B. burgdorferi B31. Due to homologous recombination (double crossover) between the sequences of pXLF11303 and the native ospAB locus in B. burgdorferi B31, the ΔospB::kan fragment is inserted into the genome, resulting in the generation of the ospB mutant (ospB −). For the generation of the OspB complemented mutant, the PospAB and ospB gene were PCR-amplified from B. burgdorferi B31 total genomic DNA and cloned into the multiple cloning site (MCS) of the shuttle vector pKFSS1 [40], resulting in the construct pFGN1 (bottom diagram). The relevant structures of the plasmid and genome are shown. Arrows represent positions of the oligonucleotides used for the PCR analysis. Primer names are retained as shown in Table 1. Vertical lines represent the restriction enzyme sites. E, EcoRI; N, NotI; and P, PstI.
(B) PCR analyses of genomic DNA isolated from spirochetes were performed to confirm the inactivated ospB locus. wt, the wild-type isolate; ospB, the ospB mutant; ospB − , recovered-spirochetes recovered from mice infected with the ospB mutant; ospB −/pFGN1, the OspB complemented mutant; M, 1-kb DNA ladder; C in (B and E) refers to PCR reactions without template DNA.
(C) RT-PCR analysis of ospA, ospB, and flaB transcripts in spirochetes grown in BSK-H media. Shown is a gel image of RT-PCR reactions performed with (+RT) and without (−RT) reverse transcriptase. C refers to RT-PCR reactions without cDNA.
(D) SDS-PAGE (top) and immunoblot (bottom) analysis of whole-cell lysates of spirochetes. Arrows indicate the expression of OspA, OspB, and FlaB. Immunoblotting analysis performed with monoclonal antibodies directed against OspB (mAb B22J), OspA (C3.78), and FlaB (H9729) were reported previously [22,50].
(E) PCR analyses of genomic DNA to confirm the OspB complementation.
(F) Restriction digestion of pFGN1 plasmid recovered from the OspB complemented mutant (pFGN1-recovered) and plasmid controls pFGN1 and pKFSS1. Whole-cell lysate from the OspB complemented mutant was transformed into E. coli DH5α-competent cells and transformed clones were selected in the presence of spectinomycin (50 μg/ml). Plasmids isolated from E. coli cells were digested with NotI or EcoRI and PstI. Expected sizes of restrictive fragments are (i) 5,638 bp and 1,906 bp for NotI digestion of pFGN1; (ii) 5,638 bp and 453 bp for NotI digestion of pKFSS1; (iii) 3,840 bp, 2,413 bp, and 1,291 bp for EcoRI-PstI digestion of pFGN1; and (iv) 3,635 bp, 2,413 bp, and 43 bp for EcoRI-PstI digestion of pKFSS1.