Figure 5. FBF dose responses to isoproterenol in the individuals who also participated in the previous study following normal sodium intake (150 mmol day−1).
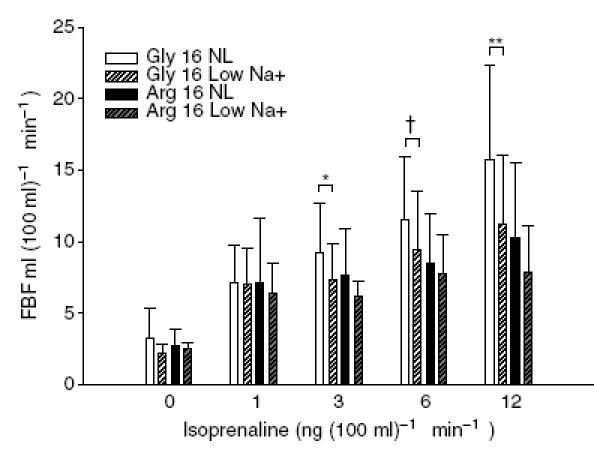
FBF response to isoprenaline was found to be dependent on genotype (P = 0.02, genotype-by-dose interaction) and diet (P = 0.02, diet-by-dose interaction). Supplemental genotype-specific analysis demonstrates that the 12 Gly16 homozygotes had a reduction in the FBF response to isoprenaline following 5 days of dietary sodium restriction at 3, 6 and 12 ng (100 ml tissue−1 min−1) (*P = 0.04, †P = 0.08 and **P = 0.007, respectively, paired t test). The FBF responses in the Arg16 group were also decreased with dietary sodium restriction, but this was not significant (P = 0.18 for all). From an analysis restricted to the maximum dose of isoprenaline, significant main effects were detected for diet (P = 0.006) and genotype (P = 0.044) with non-significant genotype-by-diet interaction (P = 0.364). Error bars denote s.d.
