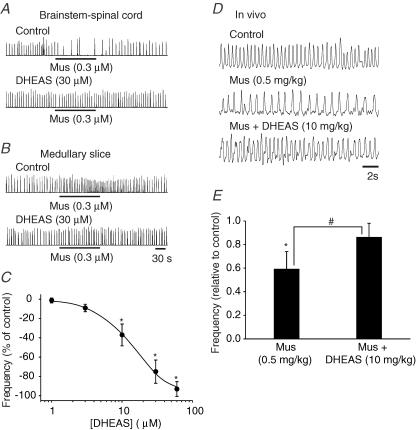
Figure 6. Effects of DHEAS on muscimol-induced changes of respiratory frequency in vitro and in vivo.
A, rectified and integrated suction electrode recordings of C4 ventral root activity in a P0 brainstem–spinal cord preparation. The inhibition of respiratory frequency by muscimol (Mus) was antagonized by DHEAS. B, rectified and integrated suction electrode recordings of XII nerve roots in a P0 medullary slice preparation. The muscimol-induced increase of respiratory frequency in 9 mm [K+]o bathing solution was antagonized by DHEAS. C, dose–response curve for the DHEAS blockade of muscimol-induced effects of respiratory frequency in brainstem–spinal cord and medullary slice preparations. Each data point was from five to eight P0 preparations. D, the effects of i.p. administration of muscimol (0.5 mg kg−1) to an unanaesthetized P0 rat pup. The muscimol-induced depression of breathing was antagonized by DHEAS (10 mg kg−1). E, population data showing changes in respiratory frequency relative to control for each of the drug protocol administrations shown in D. Each data point was from four P0 preparations. * indicates significant difference relative to control (P < 0.05); # indicates significant difference between groups (P < 0.05). Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (s.d.)