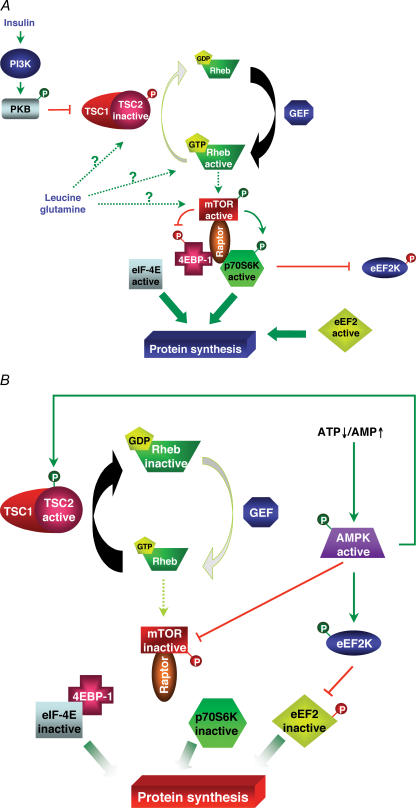
Figure 2. Diagrammatic representation of signalling involved in the regulation of the mTOR/p70S6K pathway by AMPK.
A, both insulin and amino acids stimulate the mTOR/p70S6K pathway to promote protein synthesis. Insulin, by activating the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway, inhibits TSC2, and so, via the activation of Rheb, induces mTOR activation. On the other hand, the pathway used by amino acids like leucine or glutamine to activate the mTOR pathway is still not well defined. Once activated, mTOR, with the participation of Raptor, is able to phosphorylate 4EBP-1 and p70S6K. B, activated AMPK is able to phosphorylate and activate both TSC2 and eEF2K. Moreover, AMPK can inactivate directly mTOR. GEF: guanylate exchange factor.