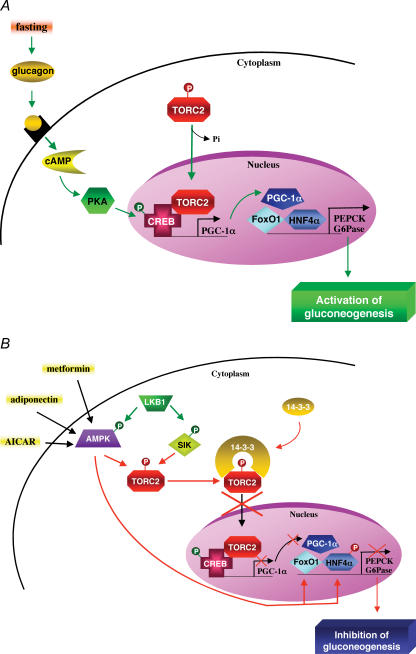
Figure 4. Transcriptional control of gluconeogenesis by TORC2 and AMPK.
A, in response to fasting, the cAMP-responsive CREB coactivator TORC2 controls the gluconeogenic programme in liver via its nuclear translocation and association with CREB transcription factor, driving the expression of the PGC1α coactivator. Expression of the coactivator PGC-1α in turn drives the transcription of key gluconeogenic enzymes such as PEPCK and G6Pase in association with the transcription factor HNF4α and the forkhead family activator FoxO1. B, activity of TORC2 is controlled by AMPK and AMPK-related kinase SIK phosphorylation, which determines whether TORC2 becomes localized in the nucleus. Phosphorylated TORC2 is sequestered in the cytoplasm via a phosphorylation-dependent interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. Moreover, AMPK can also control gluconeogenic gene transcription by regulating stability or degradation of HNF4α and FoxO1 transcription factors.