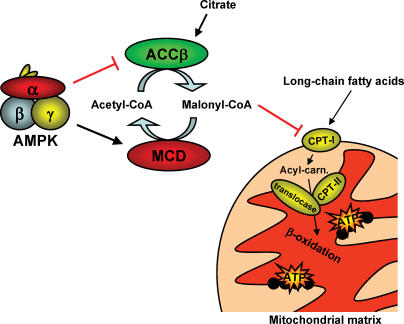
Figure 3. The mechanism by which AMPK is believed to stimulate fatty acid oxidation in the mitochondrial matrix.
Production of malonyl-CoA is reduced by inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase-β activity (ACCβ) and possibly by activating malonyl-CoA decarboxylase (MCD) activity. Since malonyl-CoA inhibits carnitine palmitoyl transferase-I (CPT-I) activity, the reduction in malonyl-CoA content will relieve CPT-I from its inhibition leading to increased mitochondrial fatty acid uptake and oxidation. Red oval arrow: inhibition/deactivation. Acyl-carn: acyl-carnitine.