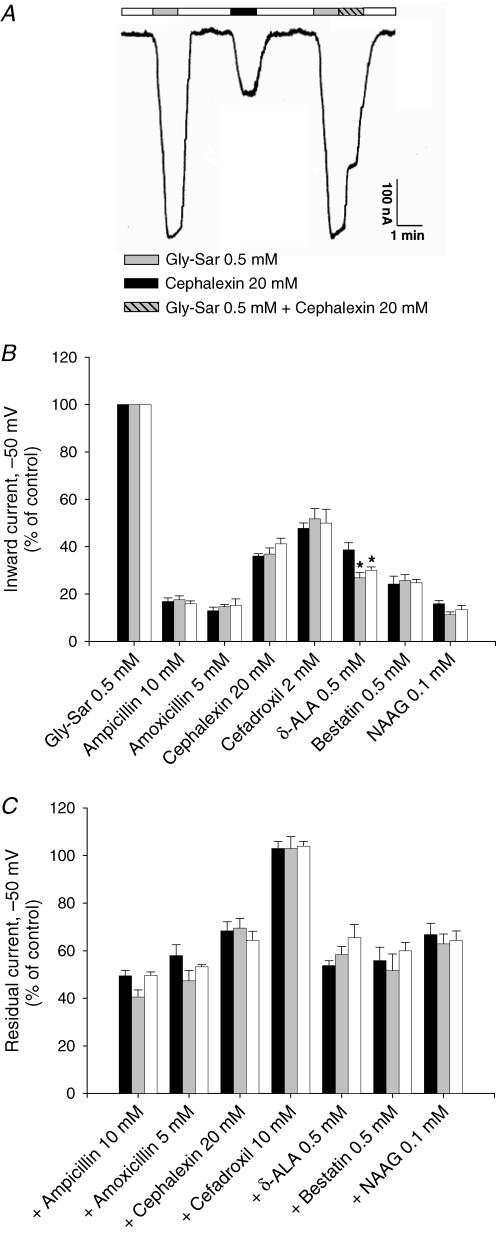
Figure 3. Substrate-induced inward currents in X. laevis oocytes expressing hPEPT1.
substrate-induced inward currents in X. laevis oocytes expressing hPEPT1. Between 4 and 7 days postinjection with transporter cRNA, oocytes were mounted in a two-microelectrode voltage-clamp system, superfused with Na+buffer at pH 5.0 and held at −50 mV. Currents in response to the addition of Gly-Sar (0.5 mm) or/and the following substrates were recorded: ampicillin (10 mm), amoxicillin (5 mm), cephalexin (20 mm), cefadroxil (2 or 10 mm), d-aminolevulinic acid (d-ALA) (0.5 mm), bestatin (0.5 mm) and N-acetyl-Asp-Glu (NAAG) (0.1 mm). A, individual trace for Gly-Sar and the β-lactam antibiotic cephalexin in WT hPEPT1. B, inward currents evoked by Gly-Sar and the selected compounds in oocytes expressing WT (black bars), S117N (grey bars) or G419A (white bars) hPEPT1. C, effect of the same drugs on inward currents evoked by 0.5 mm Gly-Sar. Results were normalized to the current evoked by 0.5 mm Gly-Sar: 240 ± 14 (WT), 241 ± 22 (S117N) and 232 ± 18 nA (G419A). Data are shown as means ± s.e.m. for at least three oocytes from different donor frogs; in each experiment, the same oocyte was used to test all compounds. *Significant difference between WT and variant hPEPT1s (P > 0.05).