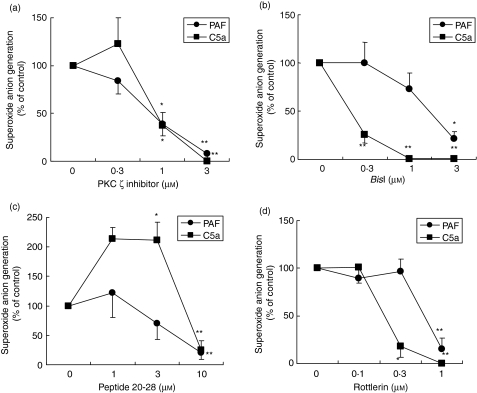
Figure 1.
Effects of protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors on superoxide anion (O2–) generation by human eosinophils. Purified human eosinophils in human serum albumin-coated wells (2·5 × 105 cells/tube) were stimulated with platelet-activating factor (PAF) (1 µm) or complement 5a (C5a) (100 ng/ml) after preincubation with each PKC inhibitor [ (a) PKC ζ inhibitor; (b) bisindlolylmaleimide I (BisI); (c) PKC inhibitor peptide 20-28; (d) rottlerin] for 10 min at 37° and then prewarmed at 37° for 5 min with 2-methyl-6-(p-methoxyphenyl)-3,7-dihydroimidazo-[1,2-a] pyrazin-3-one (MCLA). The O2– generated for 30 min after stimulation by PAF or C5a is presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) for four to 11 experiments. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; significant differences compared with cells stimulated with PAF or C5a in the absence of PKC inhibitors. O2– production in the absence of drug was as follows: PAF, 354·5 ± 41·1; C5a, 120·5 ± 23·9 (× 104 counts; mean ± SEM; n = 11–14).