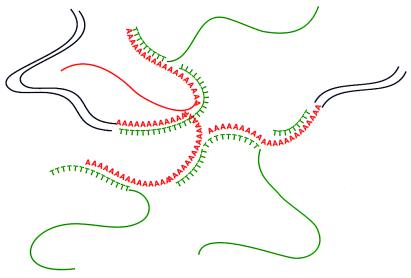
Figure 1.
Model for the formation of double-strand poly(dA)/poly(dT) complex during hybridization. Oligo(dT) priming in reverse transcription generates cDNAs with poly(dA/dT) sequences at the 3′ end. During the normalization or subtraction reaction, hybridization between poly(dA)/poly(dT) sequences among cDNA templates causes the formation of tangled double-strand hybrids. The removal of these hybrids causes the loss of many unrelated templates.