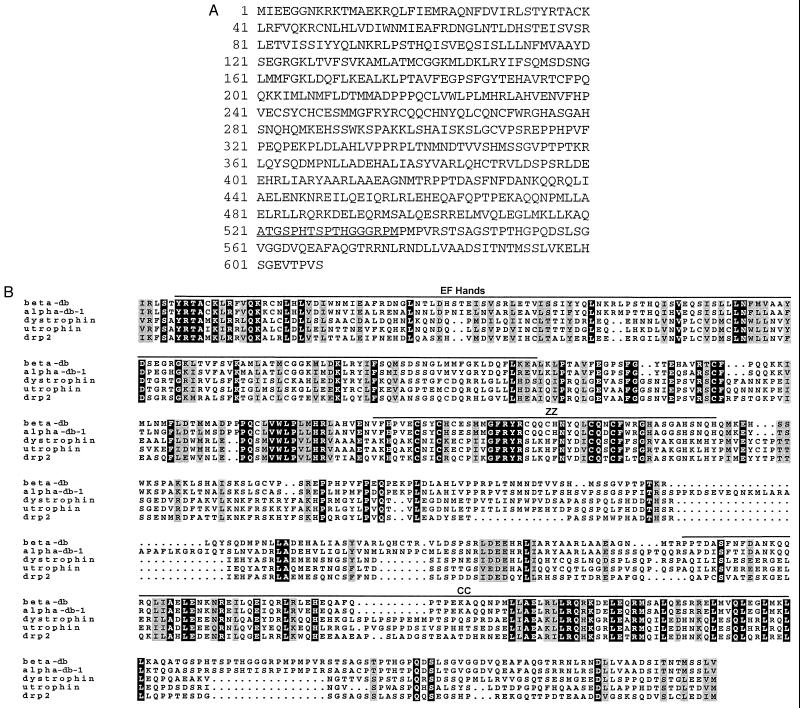
Figure 1.
(A) The primary sequence of mouse β-dystrobrevin. The deduced amino acid sequence of the largest cDNA clone expressed in both brain and kidney is shown. The underlined amino acids correspond to the sequence used to make the β521 peptide antibody. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the dystrophin-related protein family. Sequences of murine β-dystrobrevin (amino acids 30–596), the muscle-expressed isoform of α-dystrobrevin 1 (amino acids 30–629), dystrophin (amino acids 3094–3653), G-utrophin (amino acids 413–966), and human DRP2 (amino acids 395–931) were aligned by using the program pileup (GCG version 8.0). The sequences were shaded by using the program boxshade. The dark shading represents amino acid identity between all five proteins whereas the lightly shaded sequences represent amino acid similarities at a given residue. The positions of the EF hands, ZZ domain, and CC domains are indicated by lines.