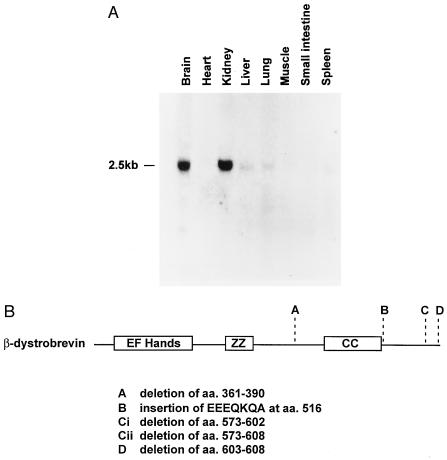
Figure 2.
(A) Expression of the β-dystrobrevin mRNA in mouse tissue. Northern blot of total RNA prepared from different mouse tissues hybridized with a 1.2-kb partial cDNA probe (m13c1) encoding the last 306 amino acids and part of the 3′ untranslated region of β-dystrobrevin. This probe detects a 2.5-kb transcript and does not detect α-dystrobrevin encoding transcripts under the conditions used for hybridization and washing. (B) Alternative splicing of the β-dystrobrevin transcript. Diagrammatic representation of the β-dystrobrevin protein and the sites that are alternatively spliced. Alternative splicing at sites C and D generates proteins with different C termini. The majority of clones isolated from the kidney cDNA library kidney contain exons C and D whereas in brain most cDNAs lack one or both of these regions.