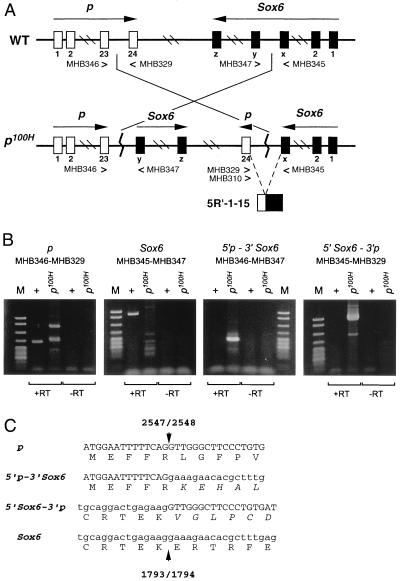
Figure 2.
(A) A schematic diagram of the p locus and the Sox6 locus on mouse chromosome 7. WT, wild type; p100H, p100H mutant. Primers used for RT-PCR are listed underneath each exon (23, 24, x, y, z). Nucleotide sequences of the primers are described in Materials and Methods. 5′R-1–15 is the first chimeric cDNA clone isolated and was used to identify the inversion breakpoints in the p100H mutation (see text). (B) RT-PCR products amplified from wild-type (+) and the p100H homozygote (p100H) brain cDNA using primers listed. +RT and −RT represent synthesis with or without RT, respectively in a cDNA reaction. Sizes of the marker standard fragments (M: pBR322 MspI digest; New England Biolabs) are from the top: 622 bp, 527 bp, 404 bp, 307 bp, 238/242 bp, 217 bp. The expected sizes of the RT-PCR products are: 292 bp for p, 575 bp for Sox6, 224 bp for 5′p-3′Sox6, and 643 bp for 5′Sox6-3′p. The two fragments seen in p100H (+RT) lane of p were cloned and sequenced. Both fragments (327 bp and 480 bp) have no significant sequence matches with the p gene except for the primer sequences and are therefore artifactual. (C) Amino acid sequence in the vicinity of the breakpoints. The predicted amino acid sequences of the chimeric transcripts are shown below the nucleotide sequence. Arrowhead indicates the breakpoint, and the numbers above and below it correspond to nucleotide numbers of the breakpoint in the p gene cDNA (GenBank accession no. M97900) or the Sox6 gene cDNA (GenBank accession no. U32614).