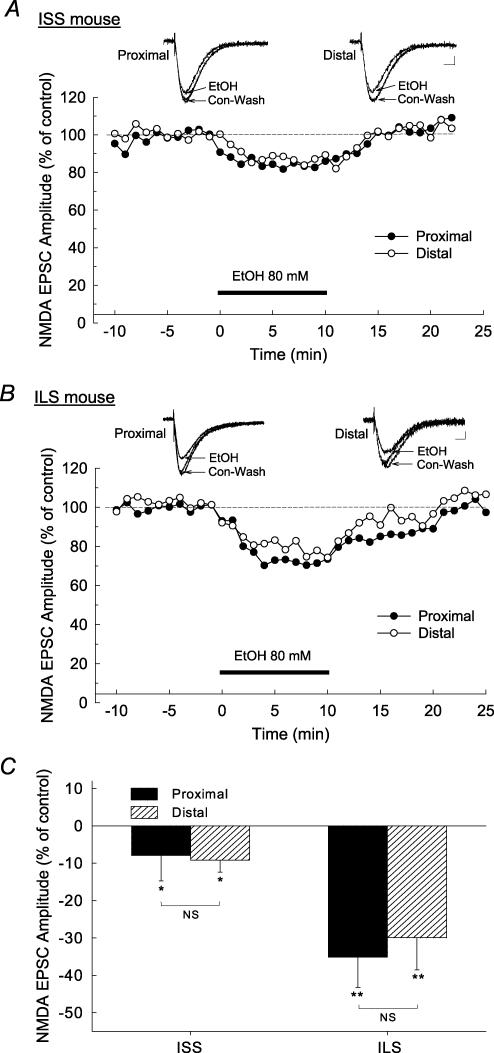
Figure 4. Acute ethanol superfusion produced differential inhibition in NMDA EPSCs in ISS and ILS mice.
Responses were pharmacologically isolated using the competitive GABAA receptor antagonist, BMI (30 μm) and the AMPA receptor antagonist, CNQX (30 μm), and representative signals are indicated as insets above time courses in A and B. A, representative time course of the effect of 80 mm ethanol on the amplitude of proximally and distally evoked NMDA EPSCs recorded in pyramidal neurons from ISS mice. Ethanol produced only a small inhibition of NMDA EPSCs in the proximal and distal subregions of the hippocampus in ISS mice. B, representative time course of the effect of 80 mm ethanol on the amplitude of proximally and distally evoked NMDA EPSCs recorded in pyramidal neurons from ILS mice. In this mouse strain, 80 mm ethanol causes marked reductions in proximal and distal NMDA EPSCs. C, composite data for the overall effects of ethanol (80 mm) on proximal and distal NMDA EPSCs from ISS and ILS mice. Scale for insets in A and B, 15 ms, 10 pA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.