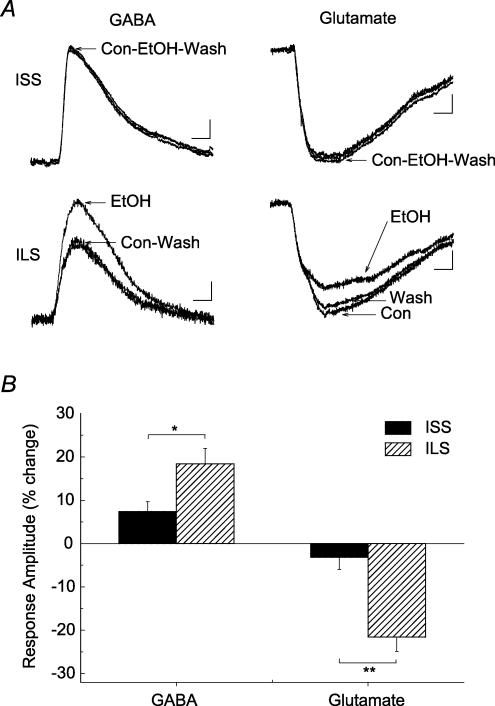
Figure 9. Ethanol enhances the GABA-evoked GABAA receptor-mediated response and inhibits the glutamate-evoked NMDA receptor-mediated response in hippocampal CA1 neurons from ILS but not ISS mice.
A, representative current traces from hippocampal CA1 neurons from ILS and ISS mice. Brief local applications of GABA (10 mm) in the presence of CGP-52432 (0.5 μM) or glutamate (0.3 mm, plus 3 μm glycine) in the presence of CNQX (20 μm) produced robust GABAA receptor-mediated or NMDA receptor-mediated responses, respectively. Ethanol (80 mm) (20 μm) perfusion enhanced GABAA responses and inhibited NMDA responses in neurons from ILS mice. This concentration of ethanol did not significantly alter these responses in neurons from ISS mice. B, summary data showing that ethanol significantly affected these agonist-evoked responses in neurons from ILS but not ISS mice. Number of cells in these experiments: ISS, GABAA, n = 6; ISS, NMDA, n = 6; ILS, GABAA, n = 8; ILS, NMDA, n = 6. Scales for GABA-evoked responses: ISS, 50 ms, 20 pA; ILS, 50 ms, 10 pA. Scales for glutamate-evoked responses: ISS, 50 ms, 15 pA; ILS, 50 ms, 15 pA.