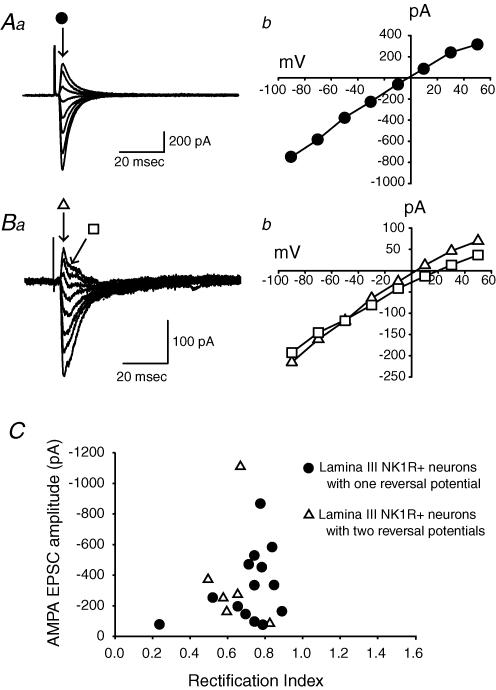
Figure 6. The synapses between primary afferents and NK1R+ neurons in lamina III/IV show two types of evoked EPSCs.
Aa, an example of the first type of evoked AMPA EPSCs at different holding potentials. • indicates the time point to measure the peaks of the AMPA EPSCs. Ab, peak current amplitudes are plotted as a function of membrane potential. Ba, an example of another type of AMPA EPSC. Evoked AMPA EPSCs showed two distinct reversal potentials. ▵ and □ indicate the time points to measure the first and second peak amplitudes of the AMPA EPSCs, respectively. Bb, peak I–V curves for the first and second peak amplitudes. C, distribution of AMPA EPSC amplitudes as a function of rectification index for two groups of lamina III/IV NK1R+ neurons.