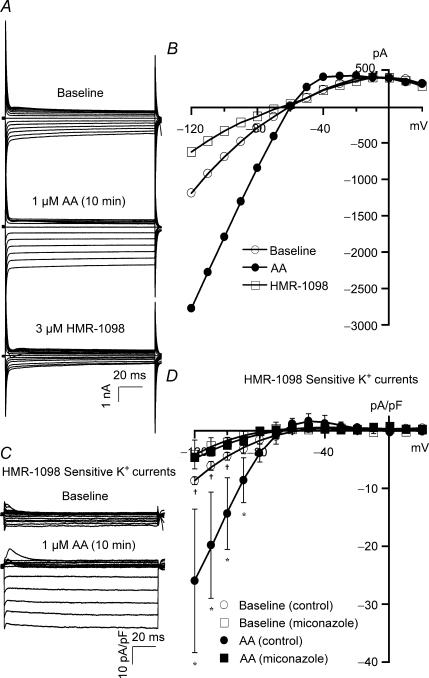
Figure 1. Effects of AA metabolites on cardiac KATP channel activities in rat ventricular myocytes.
A, whole-cell total K+ currents were elicited from −120 mV to +20 mV at a holding potential of 0 mV at increments of 10 mV in control rat ventricular myocytes. K+ currents were activated by 1 μm AA, reaching steady state in 10 min, and then exposed to 3 μm HMR-1098. B, I–V relationships of total K+ currents at baseline, in response to 1 μm AA, and 3 μm HMR-1098. C, HMR-1098-sensitive K+ currents (cardiac KATP currents) were obtained from the current tracings in A by digital subtraction of the residual currents after exposure to HMR-1098 (3 μm) from the total K+ currents. KATP currents were activated by AA. D, the KATP channel I–V relationships show inward rectification with a reversal potential of −70 mV. AA (1 μm) enhanced KATP currents at all voltages negative to reversal potential (inward currents). Treatment with 10 μm miconazole reduced KATP current densities at baseline and abolished the response to AA. Each point represents the mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05 for AA versus baseline (n = 6). †P < 0.05 for baseline currents with versus without miconazole treatment (n = 5).