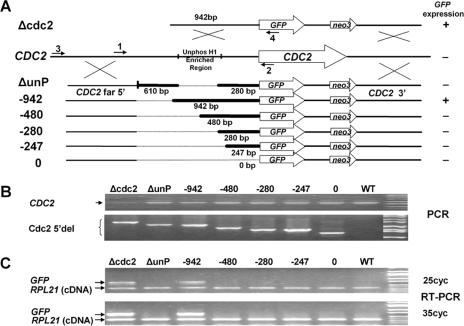
FIG. 1.
Mapping the CDC2 promoter at the CDC2 locus using GFP fusions. A. Serial deletion constructs were made using GFP as a reporter and a neo3 selectable marker inserted downstream of the 3′ UTR. Homologous recombination occurs in the 5′ region flanking the deletion (CDC2 far 5′) and the distal 3′-flanking region of the CDC2 gene to insert the reporter constructs into the endogenous CDC2 gene during somatic transformations. The CDC2 knockout construct, Δcdc2, lacking any 5′ deletion is shown at the top of the diagram. Below the endogenous CDC2 locus are the deletion constructs, with the heavy lines indicating the bases immediately 5′ of the initial ATG that are retained in the constructs. The numbered arrows indicate the primers used in panels B and C. The GFP expression status determined by RT-PCR shown in panel C is listed to the right of the deletion constructs. B. Genomic PCR using primers 1 and 2 showed the presence of the endogenous CDC2 gene (CDC2), and genomic PCR using primers 3 and 4 demonstrated that the various deletion constructs (Cdc2 5′del) localized to the endogenous CDC2 locus in the transformed cells. Shown are the ethidium bromide (EB)-stained PCR products separated on agarose gels. C. GFP expression was analyzed by RT-PCR using total RNA extracted from the above-mentioned transformants in log phase. Shown are the EB-stained RT-PCR products from 25 or 35 cycles of PCRs separated on agarose gels. The two primers for the ribosomal protein RPL21 gene span an intron, so true RT-PCR products are distinguishable from contaminating genomic DNA. Unphos H1, unphosphorylated H1.