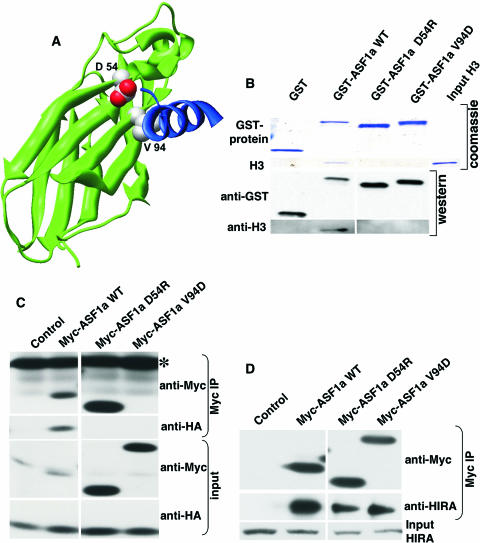
FIG. 2.
Design of ASF1a mutants deficient in histone H3 binding. (A) Mutated residues (space fill, CPK coloring) on a modeled human ASF1a/H3 structure. Residues 1 to 156 of ASF1a are shown as the green ribbon. An ASF1a-binding H3 peptide (residues 122 to 135) is shown as the blue ribbon (data are taken from reference 55; see also reference 77). (B) GST pulldown assay using GST alone or GST-tagged wild-type (WT) ASF1a and its mutants and purified recombinant histone H3. After pulldown, the washed proteins bound to resin were separated on SDS-PAGE gels and visualized either by Coomassie blue staining or by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (C) Myc-tagged wild-type ASF1a or its mutants were coexpressed with HA-tagged histone H3 in WI38 cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody (9E10), and Western blotted with the indicated antibodies. Note that Myc-ASF1aV94D comigrates with the light chain of the antibody used for immunoprecipitation (IP; marked with *) and that there is a background band in the control lane of the anti-Myc input. (D) Myc-tagged wild-type ASF1a or its mutants were expressed in WI38 cells, immunoprecipitated with the anti-myc antibody (9E10), and Western blotted with the indicated antibodies.