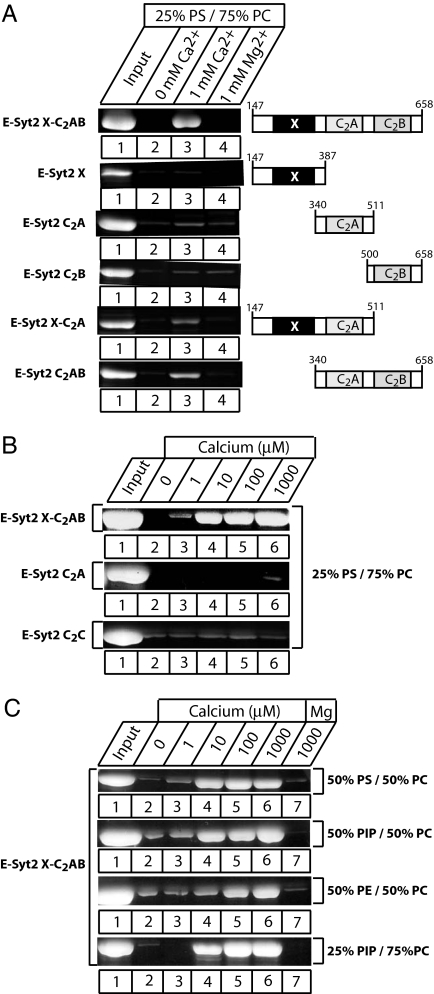
Fig. 2.
Ca2+- and phospholipid-dependent membrane binding by E-Syt2 C2 domains. (A) Recombinant GST-fusion proteins containing the E-Syt2 domains indicated on the right were used in phospholipid-binding assays. Proteins were incubated in the absence of divalent cations, in 1 mM Ca2+, or in 1 mM Mg2+ with liposomes composed of 25% PS/75% PC (wt/wt). Liposomes were pelleted by centrifugation, and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie staining. (B) Ca2+ dependence of phospholipid binding. Recombinant GST-fusion proteins containing either the E-Syt juxtamembranous X domain together with the C2Aand C2B domains (XC2AB), or only the C2A or C2C domain from E-Syt2, were incubated with liposomes composed of 25% PS/75% PC in the presence of the indicated concentrations of free Ca2+. Proteins bound to the liposomes were analyzed by centrifugation, followed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (C) Phospholipid dependence of Ca2+-dependent membrane binding of the E-Syt2 C2AB domains. Phospholipid binding of a GST fusion protein containing the E-Syt2 C2AB domains was tested at the indicated Ca2+ concentrations and in the presence of 1 mM Mg2+ (as a negative control) in liposomes with the four different phospholipid compositions shown on the right. (PIP, phosphatidylinositol phosphate; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine).