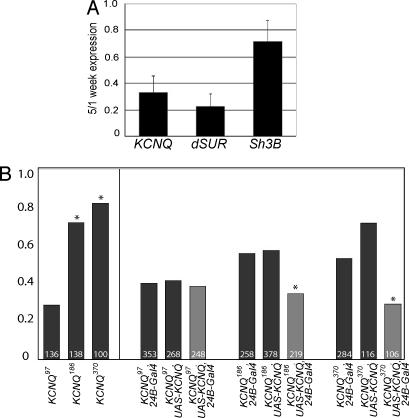
Fig. 1.
Cardiac KCNQ levels are reduced with age, and KCNQ mutants are susceptible to pacing-induced failure. (A) KCNQ RNA levels isolated from hearts dissected at 5 weeks are decreased to 33% relative to the 1-week levels (mean ± SD of three independent experiments; see also SI Fig. 5E). A control gene SH3β was only reduced to 72% of 1-week levels. (B) (Left) One-week-old KCNQ mutant flies (KCNQ186 and KCNQ370) exhibit significantly elevated heart-failure rates (∗, P < 0.01, χ2 analysis) in response to electrical pacing compared with WT controls (KCNQ97). (Right) Mesodermal overexpression of the WT KCNQ cDNA (light bars) reduces the failure rate to control levels (dark bars).