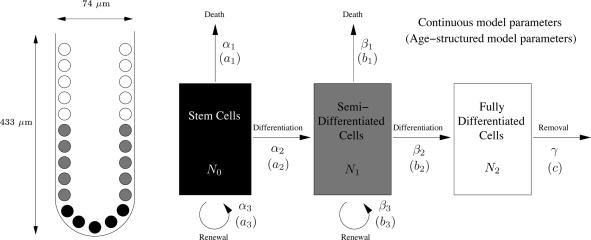
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of a colonic crypt. (Left) A schematic diagram of a crypt, with stem, semidifferentiated (transit-amplifying), and fully differentiated cell populations. The dimensions given are for a human colonic crypt according to Halm and Halm (23). (Right) A diagram showing the compartmental structure used in the model by Tomlinson and Bodmer (22). The stem cells differentiate into semidifferentiated cells, which in turn differentiate into fully differentiated cells. Each cell population can die, and the stem cells and semidifferentiated cells can renew. The parameters for the age-structured model are the proportions of the populations ai, bi, and c that are leaving the compartments, and the parameters for the continuous model are rates of conversion αi, βi, and γ.