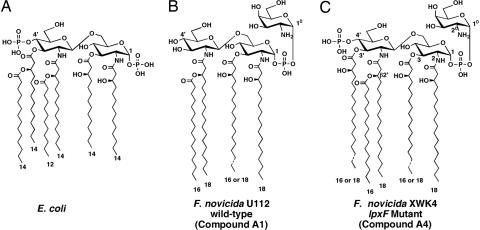
Fig. 1.
Structures of lipid A molecules synthesized by E. coli and F. novicida. (A) E. coli lipid A is synthesized by a system of nine constitutive enzymes (2), orthologs of which are present in Francisella (15). Numbers indicate the lengths of the predominant fatty acyl chains. (B) Structure of the predominant form of lipid A (compound A1) extracted from F. novicida wild-type U112 grown to late log phase at 37°C on 3% trypticase soy broth, supplemented with 0.1% cysteine (12, 48). Compound A2, which represents ≈10% of the total, is modified with a glucose residue at position 6′. (C) Structure of the predominant lipid A species (compound A4) present in XWK4, the lpxF mutant of F. novicida. When the 4′-phosphate moiety is not removed, the 3′-O-acyl chain stays in place, indicating an obligatory order of enzymatic processing. More than 90% of Francisella lipid A is free, in that it is not covalently linked to LPS (12).