Fig. 2.
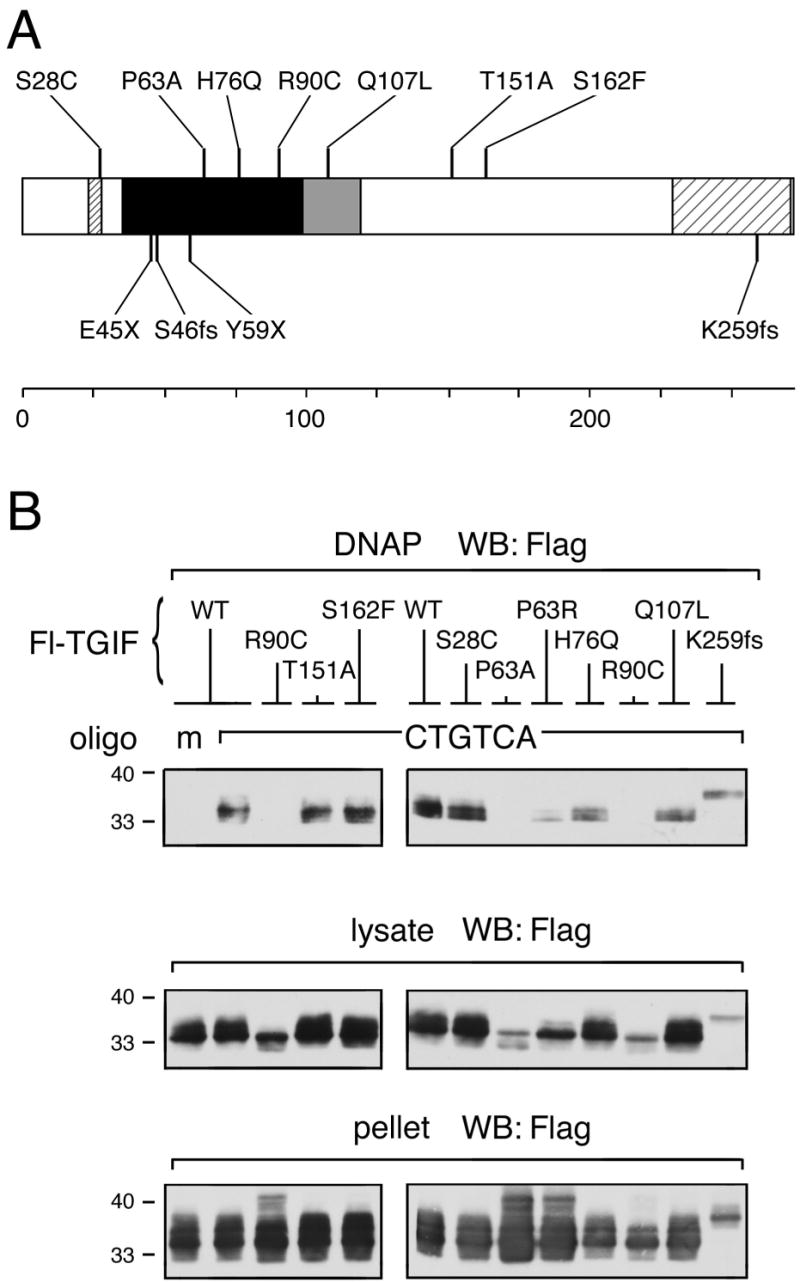
(A) Summary of the positions of the studied mutations within the TGIF protein. Note that the P63R mutation [11] was incorrect; instead, the observed sequence change predicts P63A. (B) HPE mutations in the homeodomain of TGIF affect DNA binding ability. COS1 cells were transfected with a Flag-tagged TGIF wildtype or HPE mutant construct as indicated. 36 hours after transfection, cell lysates were incubated with biotinylated double-stranded oligonucleotide containing either mutated (m) or consensus TGIF binding site (CTGTCA). TGIF protein bound to DNA was isolated on Streptavidin agarose and analyzed by western blot for the presence of TGIF. These experiments were performed repeatedly to assure consistency of the results. Portions of each lysate and pellet sample were subjected to direct western blot analysis to monitor protein expression and solubility (below).
