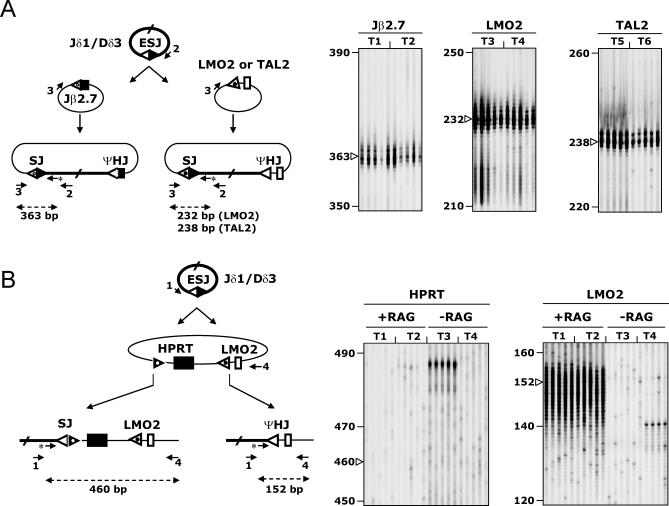
Figure 6. Ex Vivo SJ trans-V(D)J Recombination Assay with Cryptic RSS Targets.
(A) Recombination of (Jδ1/Dδ3) ESJ with Jβ2.7 12-RSS (white triangle with open dot), LMO2, or TAL2 cryptic 12-RSS (white triangle with filled dot). PE assays shown were performed on 1 μl primary PCR. Five independent PCRs from two independent transfections (T1–T2, T3–T4, and T5–T6) are shown for each junction. Similar results were obtained when LMO2 and Jβ2.7 RSSs were cloned on a single plasmid as competitive targets.
(B) Competitive recombination of (Jδ1/Dδ3) ESJ with HPRT intron 1 cryptic RSS (black triangle with white dot) versus LMO2 cryptic RSS (white triangle with filled dots). SJ, Jδ1/HPRT; ΨHJ, Jδ1/LMO2. PE assays shown were performed on 3 μl primary PCR using 30 cycles of PE. Five independent PCRs from two independent transfections performed in the presence (T1–T2) or absence of RAG-1/2 (T3–T4) are shown for each junction. Similar results were obtained when LMO2 and HPRT were cloned on separate plasmids and assayed in parallel. As described in the text, absence of specific V(D)J recombination (e.g., in absence of RAG, T3 ~485 bp) favors the emergence of nonspecific and nonrecurrent recombination events (“break-repair”).