Fig. 5.
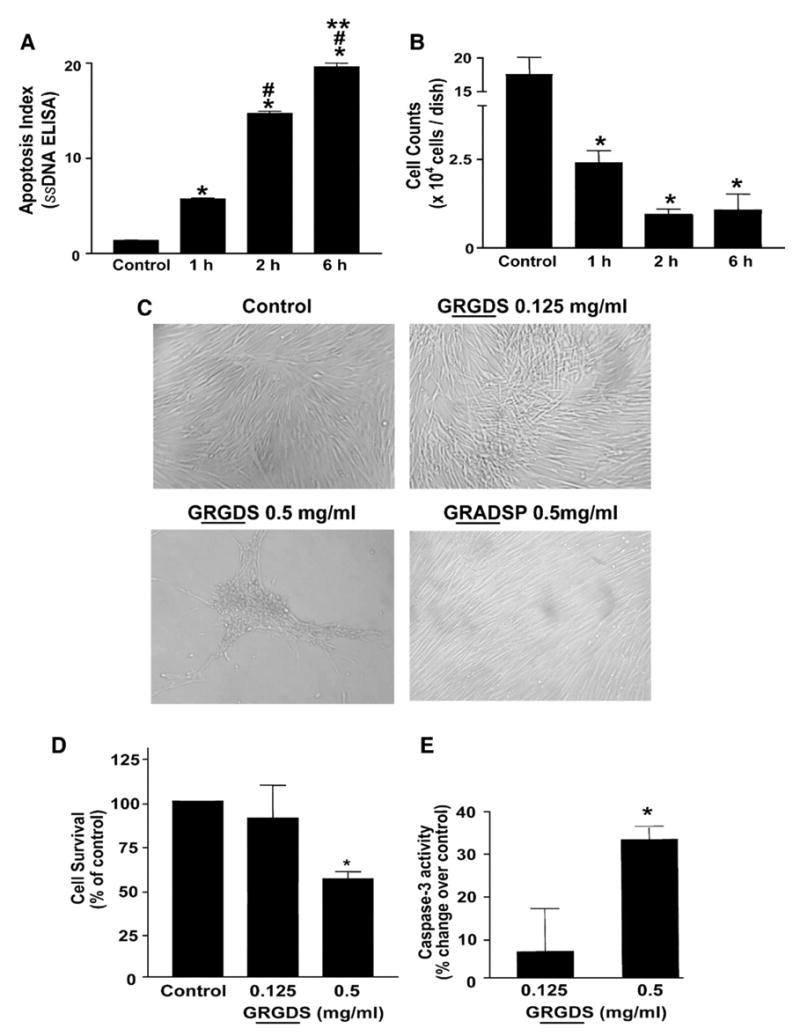
Induction of anoikis in IMR-90 fibroblasts. Quiescent IMR-90 fibroblasts were kept in suspension for the indicated time periods as described in “Material and methods”. At the end of the suspension period, cells were: (A) aliquoted into a 96-well plate for analysis of apoptosis with an ELISA for ssDNA; or, (B) allowed to re-adhere to tissue culture dishes for 3 h and numbers of attached cells were assessed by Coulter counting. Values are mean±SEM; n=3 for each time point. * p<0.001 compared to control, # p<0.001 compared to 1 h, ** p<0.001 vs. 2 h. (C) Quiescent IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with soluble RGD-containing peptides (GRGDS, 0.125 mg/ml or 0.5 mg/ml) or a non-RGD containing peptide (GRADSP, 0.5 mg/ml) for 24 h and photographed under light microscopy. (D) Quiescent IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated as in (C), and cell viability was assessed at 24 h as described in Materials and methods. Values are mean±SEM; n=6 per condition and the experiment was done in triplicate. * p<0.05 compared to control. (E) IMR-90 cells were treated with soluble RGD-containing fibronectin peptides (GRGDS, 0.125 mg/ml or 0.5 mg/ml) for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were collected and equal amounts of protein were analyzed for caspase-3 activity as described in “Materials and methods”. Values are mean±SEM; n=3 per condition and the experiment was repeated 3 times with similar results. * p<0.01 compared to control.
