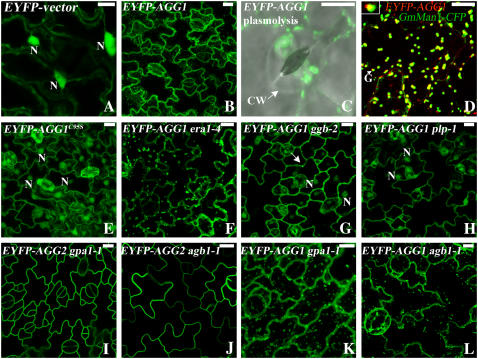
Figure 4.
Subcellular localization of EYFP tagged AGG1. Projection of multiple stacks taken from the lower epidermis of cotyledon or leaf is presented for every section except A and D. The images for the guard cells are an overlay of DIC (gray) and EYFP (green). A, EYFP-vector is cytosolic as evidenced by the bright nuclei and cytoplasmic strands. B, EYFP-AGG1 is associated with plasma membrane and internal membranes, with bright spots apparent. C, A guard cell from EYFP-AGG1 after plasmolysis displays aggregates of bright spots and endomembrane localization. D, EYFP-AGG1 (red) colocalizes with the Golgi marker GmMan1-CFP (green) in the middle of the Golgi stack as indicated by the merged yellow. The inset at the top left corner is from the arrow pointed at Golgi, showing the yellow merged color between the green and red. GmMan1 has been reported to locate at the cis/medial Golgi (Nebenfuhr et al., 1999). AGG1 is possibly located at the medial/trans Golgi. E, EYFP-AGG1C95S is cytosolic. F, The localization pattern of AGG1 is not altered in era1-4. G, In ggb-2, EYFP-AGG1 can be detected in the nuclei, but some bright spots still remain as indicated by the arrow. H, In plp-1 mutants, AGG1 is largely detected in the cytosol as evidenced by the bright nuclei. I, The localization pattern of AGG2 is not altered in gpa1-1. J, The localization pattern of AGG2 is not altered in agb1-1. K, The localization pattern of AGG1 is not altered in gpa1-1. L, The localization pattern of AGG1 is not altered in agb1-1. N, Nucleus; CW, cell wall; G, Golgi. All scale bars = 10 μm.