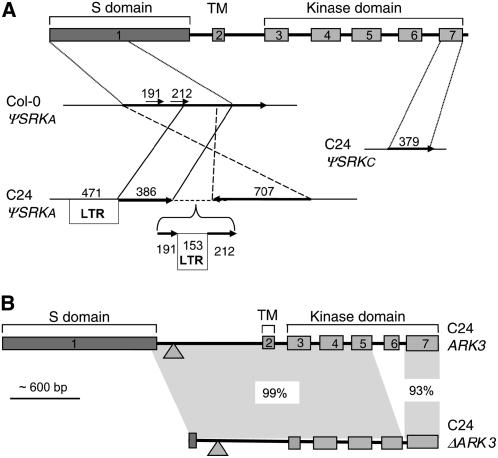
Figure 2.
Magnified View of the ΨSRK and ARK3 Sequences of the C24 S Haplotype.
(A) ΨSRK sequences. The organizations of the ΨSRKA and ΨSRKC sequences are shown in comparison to a diagrammatic view of the intron-exon structure of an SRK gene (top diagram). Regions of sequence identity are joined by diagonal or vertical lines, arrows indicate the relative orientation of the segments, and numbers above the arrows indicate the length of each segment. Note that the C24 ΨSRKC sequences correspond to exon 7, which explains the fact that C24 genomic DNA does not hybridize with a probe derived from ΨSRKC exon 1 (Table 2). The C24 ΨSRKA sequences, which correspond to 875 bp starting with the initiating ATG codon in exon 1, are highly rearranged relative to Col-0 ΨSRKA and are interspersed with LTR sequences. The unanchored contig in the C24 ΨSRKA sequence (see text) is indicated by a bracket.
(B) Duplicate ARK3 sequences. The diagram compares the structures of the complete ARK3C24 gene and the truncated ΔARK3C24 sequence. The stippled triangles indicate the location of a 54-bp deletion found in both genes relative to ARK3Col-0. The extent of sequence identity shared by different regions of the two genes is indicated.