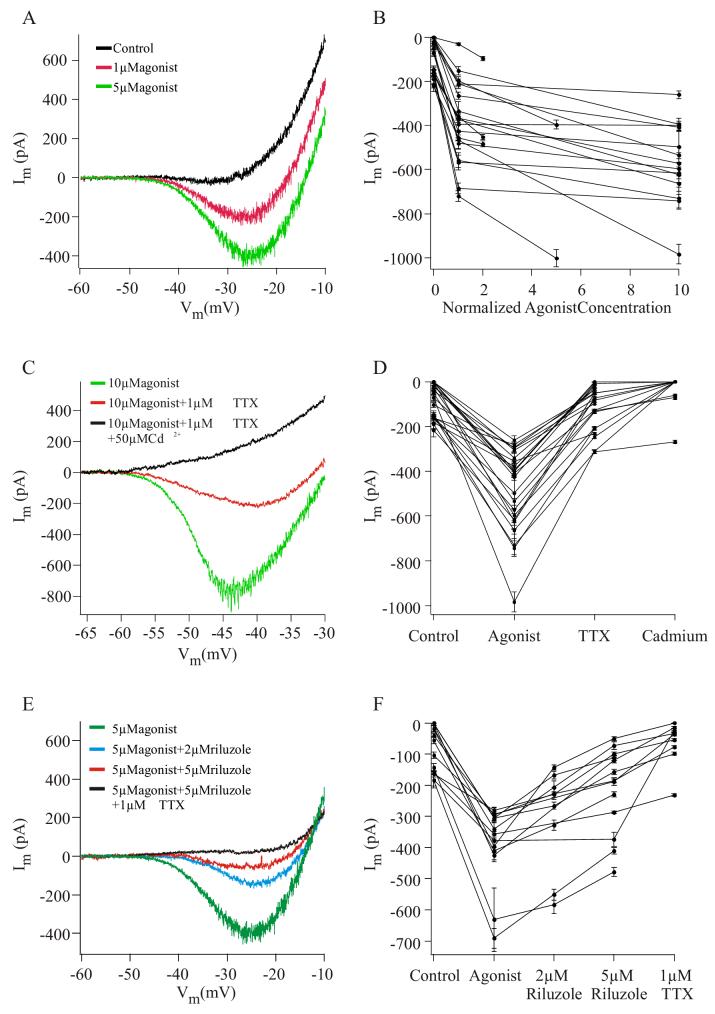
Figure 3.
5-HT2 receptor agonist facilitates a Na+ based PIC in a concentration-dependent manner.
A. Concentration-dependent facilitation of PIC magnitudes in a representative vMN. The magnitude of the PIC in control conditions (black trace, -19 ± 10 pA) was enhanced by addition of 1μM α-Me-5HT (red trace, -198 ± 20 pA). Application of 5μM agonist caused an additional increase in PIC magnitude (green trace, -396 ± 21 pA).
B. PIC magnitude as a function of normalized agonist concentration for 19 vMNs. Agonist concentrations were normalized to the lowest concentration applied to each cell. The increase in PIC magnitude from control conditions (concentration of zero) to the lowest agonist concentration was significant in each cell. Increasing the agonist concentration caused an additional significant increase in 18 vMNs. Here and in similar figures, data are presented as mean ± SD.
C. PICs in vMN have a prominent Na+ component. Application of 1 μM TTX (red trace) caused a significant reduction in the agonist facilitated PIC (green trace) in a representative vMN. Subsequent addition of Cd2+, a calcium channel blocker, completely eliminated the remaining PIC (black trace).
D. Effect of TTX and Cd2+ on facilitated PIC magnitudes, recorded from 23 vMNs. Application of 1μM TTX significantly reduced the PIC magnitude in each motoneuron. The subsequent application of 50 to 200μM Cd2+ to 13 vMNs completely suppressed the remaining PIC in 10 neurons, and significantly reduced it in the remaining 3.
E. Response of a representative vMN to riluzole. Riluzole (2 μM, blue trace; 5 μM red trace) caused a concentration-dependent reduction in the magnitude of the agonist facilitated PIC (green trace). Application of TTX completely abolished the PIC in this vMN (black trace).
F. Group data for 13 vMNs demonstrating the concentration-dependent effects of riluzole on the magnitude of the agonist facilitated PIC. In the nine vMNs tested at both concentrations, riluzole significantly reduced the PIC magnitude in a concentration-dependent manner. A similar reduction was observed in three of four vMNs tested with only 5 μM riluzole. In the nine vMNs in which it was applied, TTX caused an additional significant reduction in PIC magnitude.