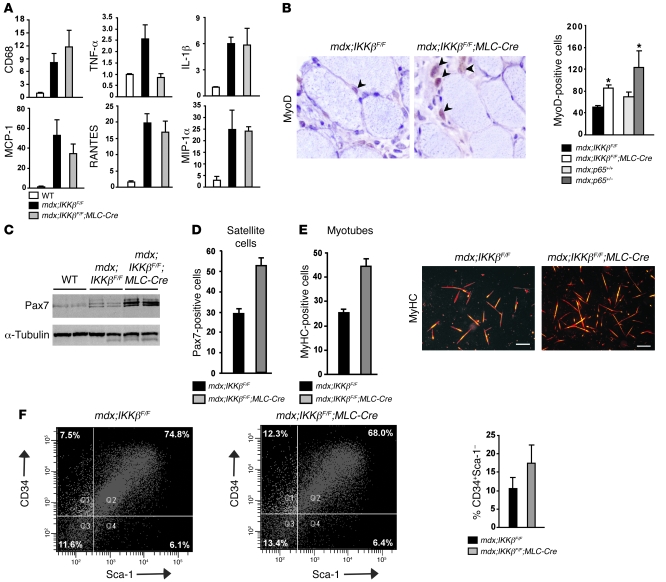
Figure 7. Muscle progenitor cells increase in mice lacking IKKβ.
Gastrocnemius or quadriceps were harvested from 4-week-old mdx;IKKβF/F and mdx;IKKβF/F;MLC-Cre mice and frozen for RNA analysis (A), cryosectioned (B), or homogenized for immunoblotting (C). (A) Real-time PCR analysis of CD68, TNF-α, IL-1β, MCP-1, RANTES, and MIP-1α (macrophage inflammatory protein 1α) obtained from 3–6 mice per group. (B) Sections as described in A or from 7-week-old mdx;p65+/+ and mdx;p65+/– mice were immunostained with MyoD and quantitated from a minimum of 20 randomly chosen fields per section in 3–4 animals per group. (C) Western blots probing for Pax7 and α-tubulin. (D and E) Satellite cells were isolated from pooled hind limb muscles from 4-week-old mdx;IKKβF/F and mdx;IKKβF/F;MLC-Cre littermates and either fixed and stained with Pax7 or differentiated for 3 days and subsequently stained with MyHC to determine myotube number normalized per mm2 area. Scale bars: 200 μm. (F) Flow-cytometric analysis from freshly isolated cells of 4-week-old mdx;IKKβF/F and mdx;IKKβF/F;MLC-Cre mice were stained with cell-surface markers CD34 and Sca-1. Graph represents averages from 2 independent experiments. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM.