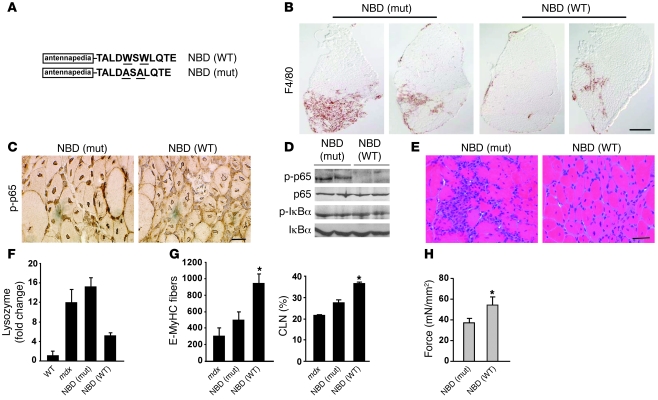
Figure 8. Pharmacological inhibition of IKK rescues the histopathology and function of dystrophic muscle.
(A) Amino acid sequence of WT or mutant (mut) NBD peptides. Underlined amino acids indicate changes from WT to mutant forms. (B) Soleus muscles from WT or mutant NBD–treated mice were stained with F4/80, and macrophages were quantitated. Scale bar: 300 μm. (C) Gastrocnemius muscles harvested from mdx mice treated for 4 weeks were sectioned and stained with either p-p65 (C) or H&E (E). Scale bars: 20 μm (C and E). (D) Lysates from mice were used for Western blots probing for p-p65, p65, and IκBα. (F) RNA was isolated from similar muscles as used for D including C57BL/10 and mdx controls, and real-time PCR was performed for lysozyme (n = 4). (G) Regeneration potential was measured by quantitating fibers with centronucleation and positive E-MyHC staining from mdx mice treated with saline or NBD peptides. (H) Force generation assessed by measuring active developed force comparing diaphragm muscles from mice treated with either WT or mutant NBD peptide for 4 weeks. Quantitative data are plotted as mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05.