Fig. 3. Loss of p57 results in an increase in dividing progenitors and ectopic cell division.
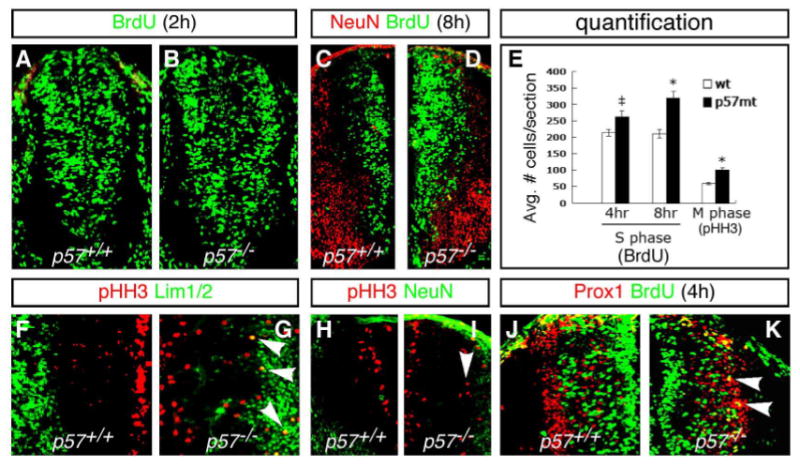
(A–D) Increased BrdU incorporation is seen in p57−/− mutants at E10.5d (B) and E11.5d (D) compared to the wild type embryos (A, C). (E) Quantification of BrdU incorporation results. There is a significant increase in BrdU incorporation in p57−/− mutants, compared to WT, after 4 and 8 hour pulses prior to sacrifice. (F–I) Expression of the G2-M marker phosphorylated Histone H-3 (pHH3) in WT and p57−/− mutants. Ectopic pHH3 expressing cells are detected laterally among Lim1/2+ (G) and NeuN+ (I) cells in the marginal zone (arrowheads). As a consequence, the total number of pHH3+ cells is significantly increased in p57−/− mutants (E). (J) In WT embryos, Prox1+ cells are not labeled after a 4-hour BrdU pulse. (K) In p57−/− null mice, a 4-hour interval following BrdU pulse labelled numerous Prox1+ cells in the lateral VZ (yellow cells marked by arrowheads). Panels (C–K) show left-right hemi-sections through p57+/+ (left) and p57−/− (right) mutant embryos. Significance: ‡p<0.05, *p<0.01.
