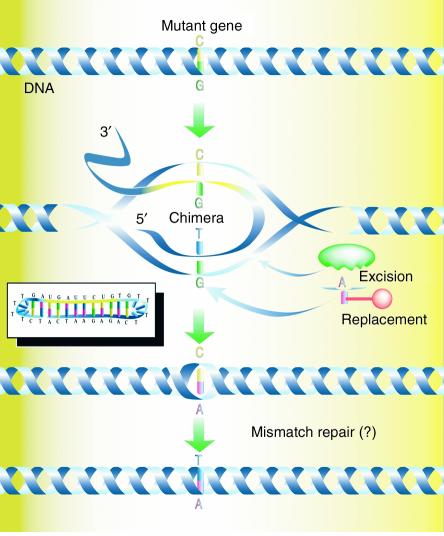
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanism of targeted gene repair directed by chimeric RNA/DNA oligonucleotides. The RNA/DNA chimera (inset) is a single-stranded oligonucleotide consisting of RNA and DNA residues. The molecule acts by annealing at the site in the target DNA, with the RNA section (yellow) hybridizing with perfect complementarity to one strand and the DNA stretch (blue) hybridizing to the other strand. A T/G base pair mismatch is formed and is acted upon by the cell’s DNA repair systems. In this case, the G residue is excised and replaced by an A to base pair with the T base provided by the chimera. The chimera dissociates, leaving behind a C/A mismatch, which is presumably corrected by the mismatch-repair system to generate a T•A base pair. Here, the action of the chimera directs the exchange of a C•G base pair with a T•A base pair. Reproduced with permission from Science’s STKE (46).