Abstract
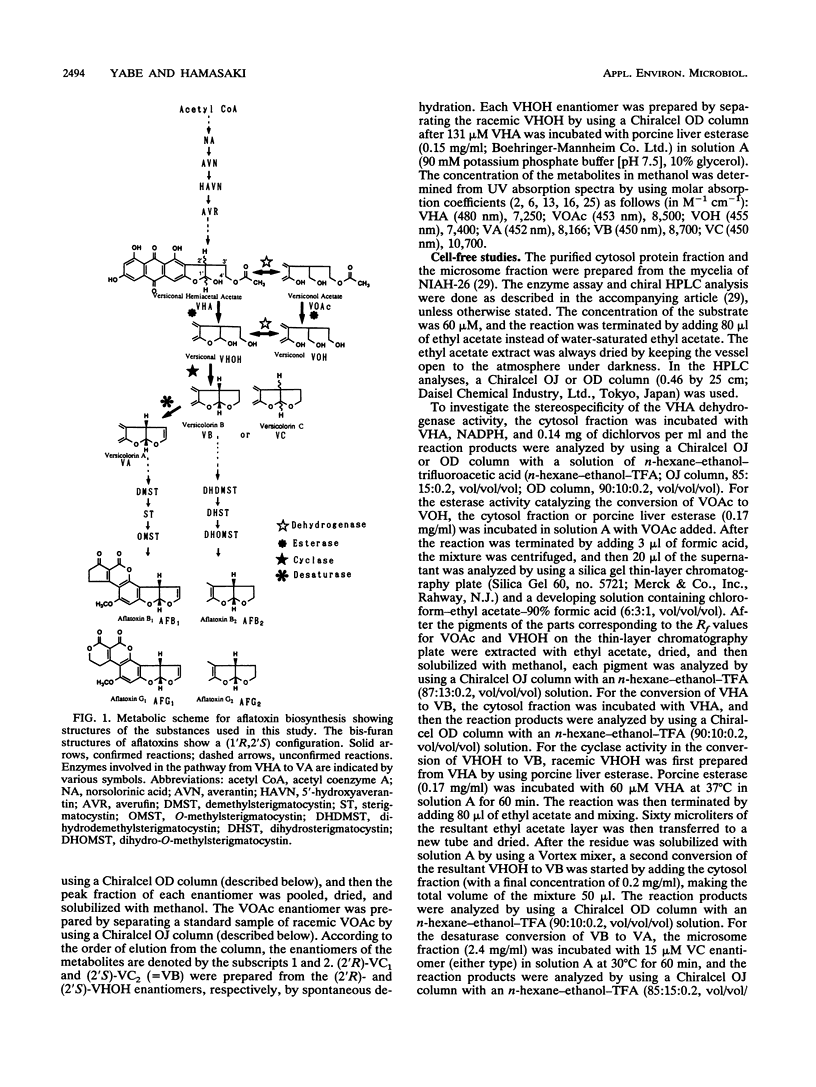
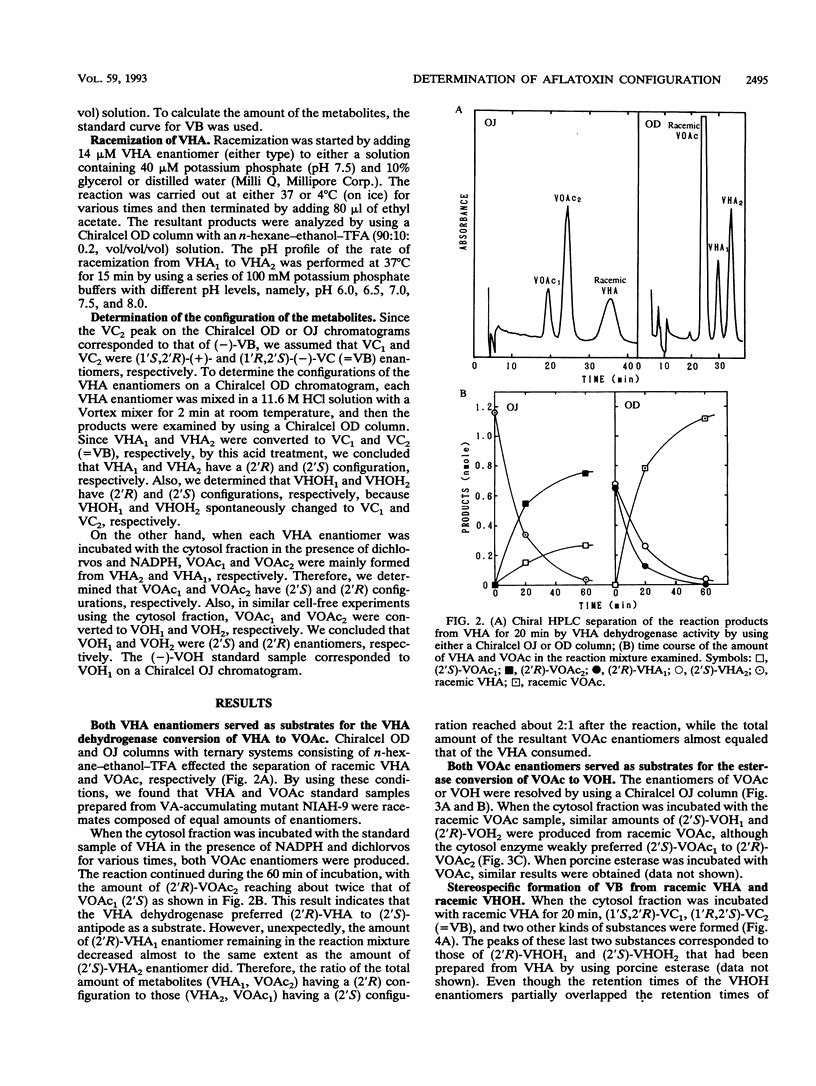
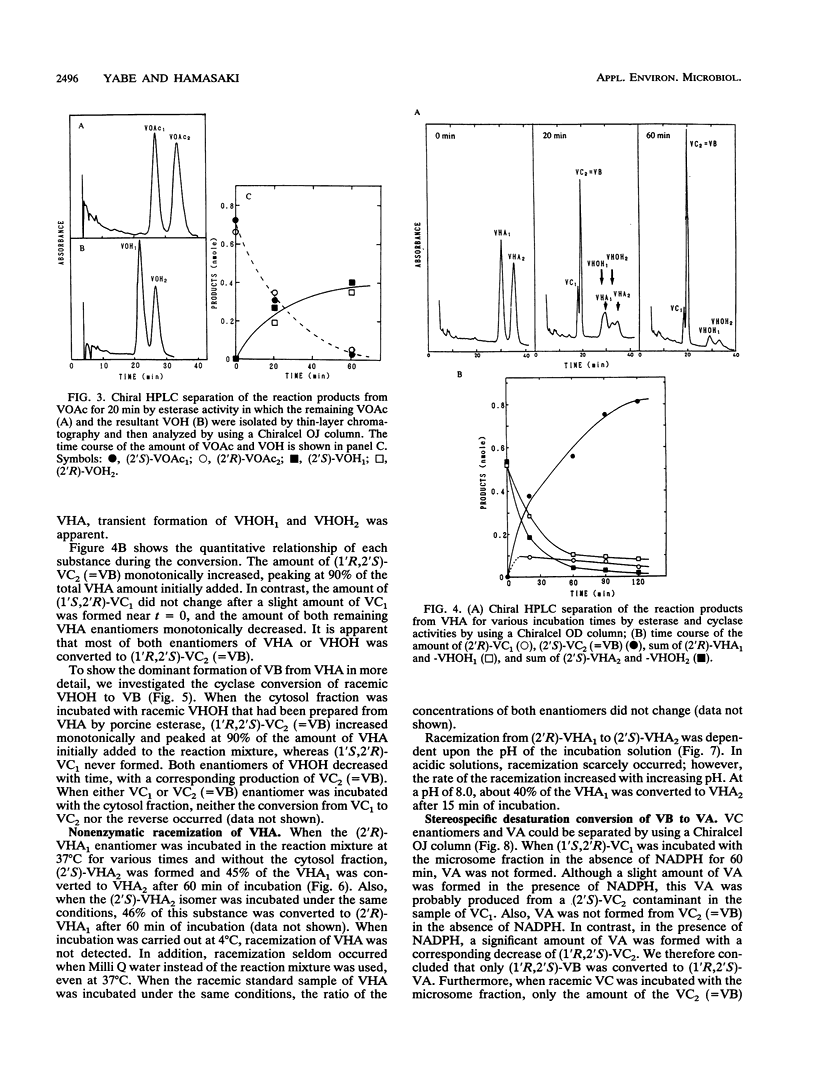
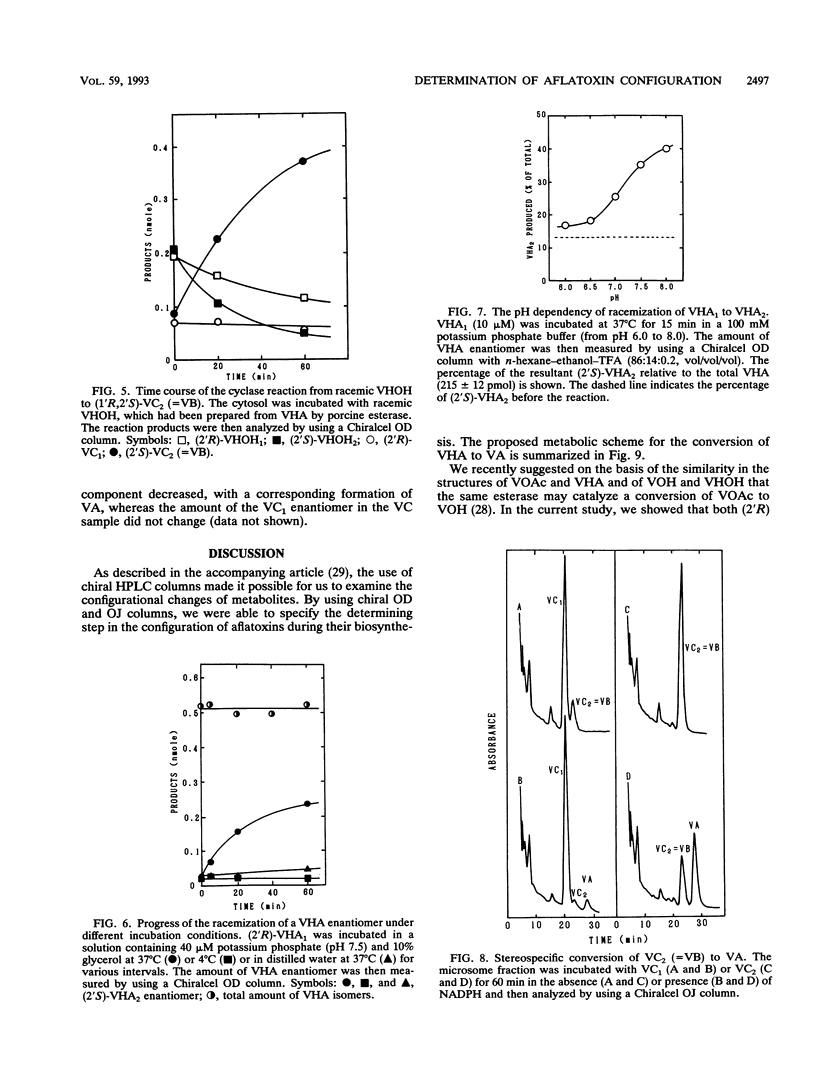
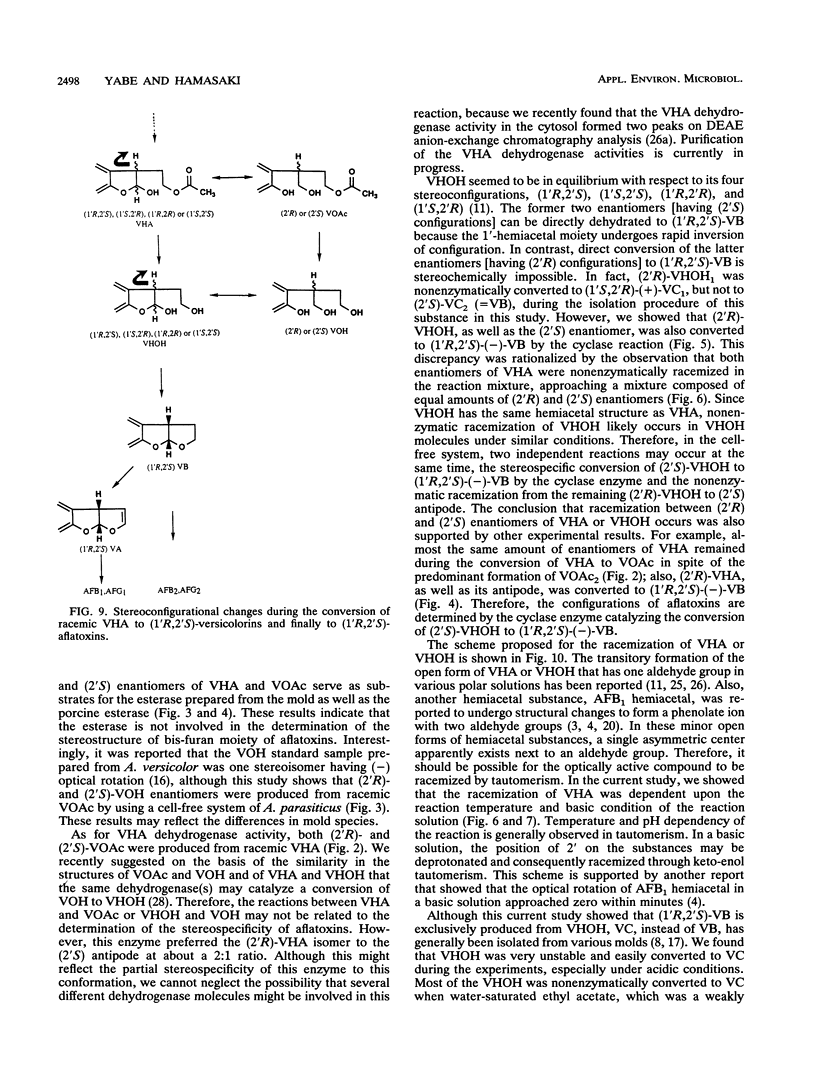
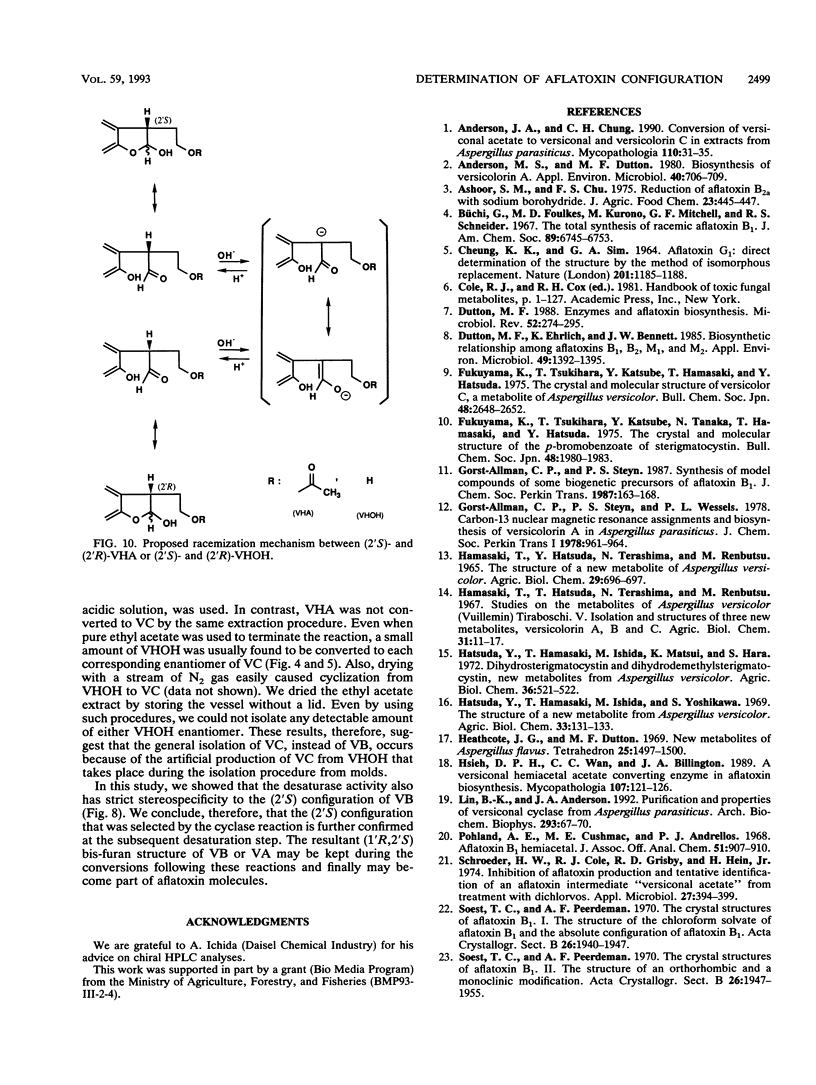
(1'R,2'S)-(-)-aflatoxins are produced from racemic versiconal hemiacetal acetate (VHA) through complicated pathways, including a metabolic grid involving VHA, versiconol acetate (VOAc), versiconol, and versiconal (VHOH), and a reaction sequence from VHOH to versicolorin A (VA) through (-)-versicolorin B (VB) [or (+/-)-versicolorin C] (K. Yabe, Y. Ando, and Y. Hamasaki, J. Gen. Microbiol. 137:2469-2475, 1991; K. Yabe, Y. Ando, and T. Hamasaki, Agric. Biol. Chem. 55:1907-1911, 1991). In this study, we examined stereochemical changes of substances formed during the conversion of VHA to VA by using chiral high-performance liquid chromatography. In cell-free experiments using the cytosol of Aspergillus parasiticus NIAH-26, both (2'S)- and (2'R)-VOAc enantiomers were formed at about a 1:2 ratio from racemic VHA in the presence of NADPH and dichlorvos (dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinylphosphate). Also, the esterase activity catalyzing the conversion of VHA to VHOH or of VOAc to versiconol did not show the stereospecificity for the 2' carbon atom of VHA or VOAc. However, when racemic VHA or racemic VHOH was incubated with the cytosol, (1'R,2'S)-(-)-VB was formed exclusively. Furthermore, only (1'R,2'S)-(-)-VB, and not (1'S,2'R)-(+) antipode, served as a substrate for desaturase activity in the microsome fraction catalyzing the conversion of VB to VA. These results demonstrate that the stereoconfiguration of bis-furan moiety in aflatoxin molecules is determined by the cyclase enzyme catalyzing the reaction from VHOH to VB, and the (1'R,2'S)-(-) configuration was further confirmed by the subsequent desaturase reaction. Remarkably, we found nonenzymatic racemization in both the (2'R)- and (2'S)-VHA enantiomers, and it was dependent upon the temperature and alkaline conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Chung C. H. Conversion of versiconal acetate to versiconal and versicolorin C in extracts from Aspergillus parasiticus. Mycopathologia. 1990 Apr;110(1):31–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00442767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. S., Dutton M. F. Biosynthesis of versicolorin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):706–709. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.706-709.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashoor S. H., Chu F. S. Reduction of aflatoxin B2a with sodium borohydride. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 May-Jun;23(3):445–447. doi: 10.1021/jf60199a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchi G., Foulkes D. M., Kurono M., Mitchell G. F., Schneider R. S. The total synthesis of racemic aflatoxin B1. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Dec 6;89(25):6745–6753. doi: 10.1021/ja01001a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEUNG K. K., SIM G. A. AFLATOXIN G1: DIRECT DETERMINATION OF THE STRUCTURE BY THE METHOD OF ISOMORPHOUS REPLACEMENT. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1185–1188. doi: 10.1038/2011185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F., Ehrlich K., Bennett J. W. Biosynthetic relationship among aflatoxins B1, B2, M1, and M2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1392–1395. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1392-1395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F. Enzymes and aflatoxin biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):274–295. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.274-295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Wan C. C., Billington J. A. A versiconal hemiacetal acetate converting enzyme in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Mycopathologia. 1989 Sep;107(2-3):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00707548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. K., Anderson J. A. Purification and properties of versiconal cyclase from Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 14;293(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Cole R. J., Grigsby R. D., Hein H., Jr Inhibition of aflatoxin production and tentative identification of an aflatoxin intermediate "versiconal acetate" from treatment with dichlorvos. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. A metabolic grid among versiconal hemiacetal acetate, versiconol acetate, versiconol and versiconal during aflatoxin biosynthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2469–2475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Matsuyama Y., Ando Y., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T. Stereochemistry during aflatoxin biosynthesis: conversion of norsolorinic acid to averufin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2486–2492. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2486-2492.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao R. C., Hsieh D. P. Step of dichlorvos inhibition in the pathway of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.52-57.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


