Fig. 5.
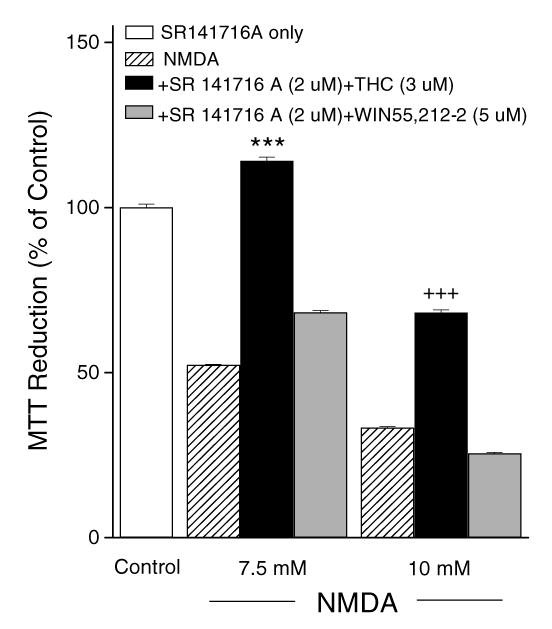
Neuroprotection induced by THC was CB1 receptor-independent. The CB1 receptor antagonist SR 141716A (2 μM) did not abolish neuroprotection by THC from NMDA-induced toxicity. *** and +++ indicate p< 0.001, respectively, as compared to 7.5 mM NMDA or 10 mM NMDA alone. Data are means ± S.E.M.
