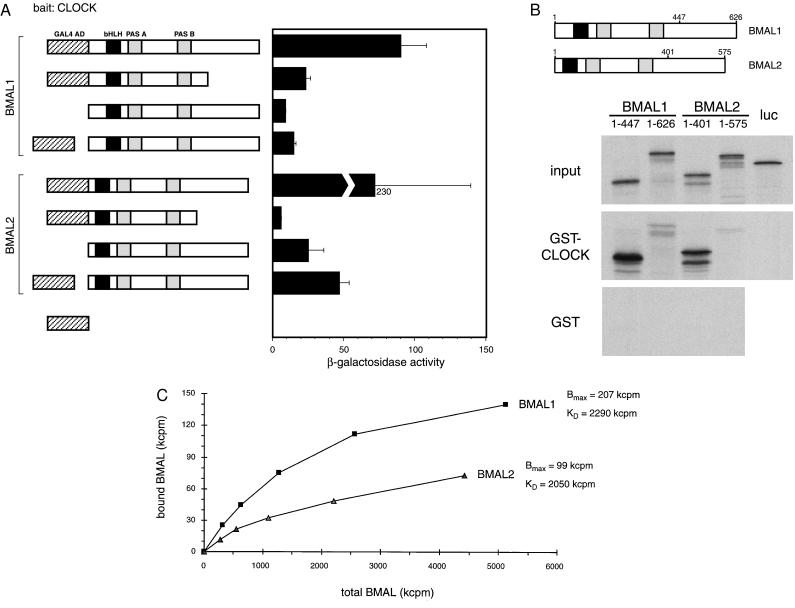
Figure 2.
Interaction of BMALs with CLOCK. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assays using various constructions in conjunction with GAL4 DBD-CLOCK. (Left) Representation of the different BMAL-based constructions. Hatched box denotes the GAL4 AD. (Right) β-Galactosidase activity, expressed in standard Miller units. The BMAL1 and BMAL2 constructions shown with a separated GAL4 AD (fourth and eighth from the top) correspond to the original clones isolated in the screen (40–1 and 40–2). (B) GST pull-down assay. Equivalent amounts of 35S-labeled complete or partial BMAL1 and BMAL2 proteins were prepared and analyzed by SDS/PAGE (input). (Lower) SDS/PAGE analysis of the proteins binding to GST or GST-CLOCK beads. Luciferase was used as a input negative control. (C) Different association affinities of zfBMAL proteins with CLOCK. 35S-labeled BMAL1 and BMAL2 were produced by in vitro transcription/translation, and radioactivity was quantified by trichloroacetic acid precipitation and scintillation counting. GST pull-down was carried out as described in Materials and Methods, with equivalent amounts of GST-CLOCK and increasing amounts of BMALs. After washes, the radioactivity remaining on the resin was quantified by scintillation counting.