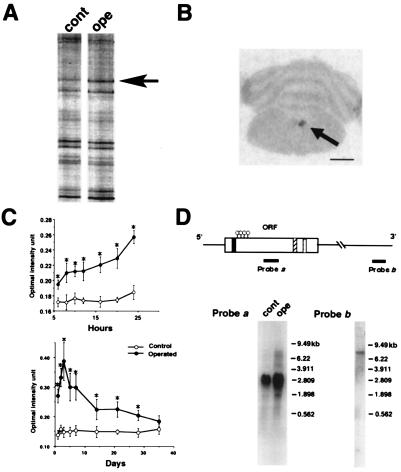
Figure 1.
Isolation of DINE by DD-PCR and its structure. (A) DD-PCR demonstrates 35S-labeled PCR products in hypoglossal nuclei of normal (cont) and operated (ope) sides (7 days after injury). The arrow indicates the differentially expressed band, which we detected in the present study. (B) Expression of the isolated cDNA fragment was further examined by in situ display. A section was obtained from a unilateral hypoglossal nerve transected-animal (7 days after surgery). The arrow indicates that the expression of the candidate gene is observed only in the hypoglossal nucleus of the injured side. (Bar = 3 mm.) (C) mRNA expression profile after hypoglossal nerve transection. The relative mRNA signal intensity in control and operated sides was measured and presented as mean +/− SD; *, P < 0.01 (ANOVA test). (D) Isolated cDNA structure encoding DINE. Closed box, predicted transmembrane domain; hatched box, zinc-binding motif; dotted box, conserved amino acids; circle, conserved cystein residues. Probe b corresponds to the initially derived DD-PCR fragment. Northern blotting was carried out by using probes a and b. In probe a, 20 μg total RNA extracted from control (cont) and axotomized (ope) hypoglossal nuclei was loaded and hybridized with probe a. In probe b, 5 μg poly(A)+ RNA from injured nuclei was loaded and hybridized with probe b.