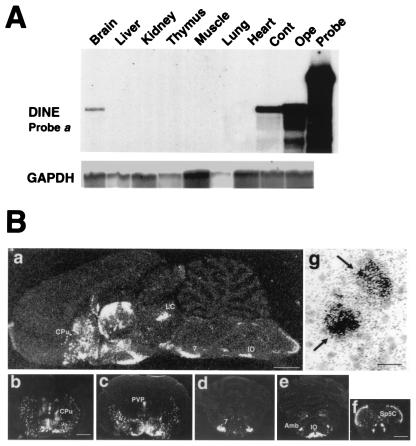
Figure 2.
Localization of DINE mRNA. (A) Tissue localization of DINE mRNA is demonstrated by RNase protection assay using probe a (Fig. 1D) and a probe for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as an internal control. (B) DINE mRNA expression in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Sagittal section (a) and coronal sections (b–f) represent DINE mRNA hybridization signal under dark-field illumination. Coronal sections at various levels: caudate putamen (b), hypothalamus and thalamus (c), pons (d), rostral part of medulla oblongata (e), and caudal part of medulla oblongata (f). Cpu, caudate putamen; LC, locus coeruleus; PVP, paraventricular thalamic nucleus; 7, facial nucleus; Amb, ambiguus nucleus; IO, inferior olive; Sp5C, spinal trigeminal tract nucleus caudalis. (Scale bar: a = 2 mm; b–e = 3 mm; f = 1 mm.) (g) Bright-field micrograph stained with thionin shows localization of mRNA on neurons (arrows). (Scale bar = 20 μm.)